Tree 20-37 m high. Leaves aggregated toward the branch-tips, the petioles 7-21 mm long; blades usually obovate or broadly oblanceolate, less frequently oblong or ? elliptic, apically obtuse to rounded or slightly emarginate, basally cuneate and symmetric or asymmetric, glabrous or essentially so, 14-31 cm long, 5-12 cm broad, with prominulous to prominent reticulation on both surfaces. Panicles 15-35 cm long, with a brown or rufescent pubescence, the bracts reduced, 1-2.5 mm long. Flowers with pedicels 1-6 mm long; calyx-segments ovate, 1-3 mm long, crassulate except at the margins; petals linear-oblong, 3-6 mm long, 1-1.75 mm broad, cream or green, + adnate to the stamen-tube; stamens (7-)10(-12), 4 much longer than the rest and extending well beyond the point at which the petals become recurved, the filaments subulate, rather conspicuously pubescent except on the extreme distal portion; ovary 0.2-0.5 mm long. Hypocarp 5-20 mm long, thickening to a breadth of 2-3 mm, twisted or sigmoid. Nut 2.5-3.5 cm long when ripe, 1-2 cm broad.
More
A large tree. It grows 40 m tall. The trunk is 2 m across. The leaves are simple and alternate and in clusters. The leaves are 30 cm long. They are rounded and wider towards the tip. The flowers are in clusters. They are greenish-white but turn pink. The fruit (nuts) are green and kidney shaped. They are 3-4 cm long. The fruit stem is spiral shaped and fleshy.
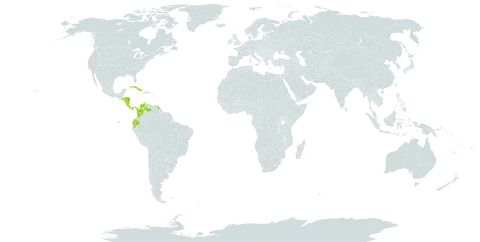
A tree of secondary forest and disturbed areas, especially frequent along the sides of streams and sometimes forming pure stands. Young plants are seldom found in mature woodland, needing sunlight to thrive.
More
A tropical plant. In Costa Rica it grows from sea level to 900 m altitude. It is often along streams in dry and open areas.