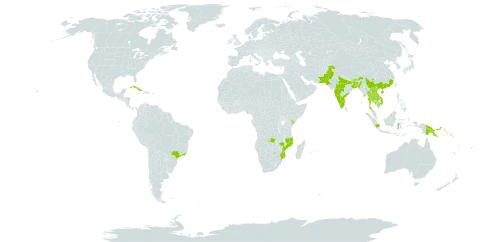
Pachycaul treelet or tree to 20(–35) m, often flowering when very small; bole to 70 cm diam., often crooked, sometimes with buttresses to l(–2) m. Bark reddish-brown, flaking; inner bark pinkish, often with white latex; sapwood white; heartwood pink. Leafy shoots 7–22 mm diam., lenticellate, sometimes myrmecophilous, subglabrous to finely fulvous tomentellous. Leaves 45–125 cm, (4–)6–10-jugate, red when young, glabrous or less often petiole, rachis and abaxial surface of leaflets and adaxial surface of veins ± brown pubescent (in sicco), the hairs simple, basally bifid or stellate or a mixture of these; petiole 5–15 cm, 6–9 mm diam., ± lenticellate, terete but greatly swollen and flattened or channelled adaxially near base. Leaflets 7.5–25 by 4–9 cm, oblong to elliptic-oblong, subcoriaceous, bases rounded to acute or attenuate, usually markedly asymmetric, apices cuspidate; petiolules 4–10 mm, the apical one to 15 mm, swollen, costae 10–12 on each side, spreading, tertiary venation sometimes prominulous in sicco. Inflorescences to 110 cm in female, 50 cm in male and hermaphrodite, but often very much shorter, ± supra-axillary; branches to 15 cm, subsquarrose; axes ± puberulous or pubescent; bracteoles c. 0.5 mm, scale-like; pedicels 0–4(–8) mm. Flowers c. 4–9 mm diam., sweetly scented (foetid, Elmer). Calyx lobes c. 2–3 mm diam., subrotund, ± pubescent without, reddish margin ciliate. Petals c. 3–5(–7) mm diam., subrotund, ± pubescent without, glabrous within, cream to yellow or bronze, sometimes tinged red, waxy. Staminal tube cream; anthers (5) 6 (8), c. 2.5–4 mm long, elliptic, apiculate, glabrous. Infructescence spicate, rarely paniculate. Capsule c. 2–4 cm diam., yellowish at first, pink or red at maturity, glabrous; pericarp sometimes with white latex, white within. Seeds 1–3, c. 17–22 mm long, plano-convex, hanging by strips of endocarp from capsule, ± covered with brownish red or orange oily aril; testa dark brown or black. 2n = 36, 76, c.150.
More
Trees or shrubs, (2-)20-30 m tall. Leaves odd-or even-pinnate, 30-60(-90) cm; leaflets (5-)9-21, opposite; petiolules (2-)6-12 mm; leaflet blades oblong-elliptic, elliptic, or ovate, (7-)17-26 × 4-10 cm with basal pair smallest, membranous when young, subleathery to leathery when mature, with visible transparent tiny spots under sunlight, both surfaces glabrous, secondary veins (8-)11-20 on each side of midvein and slender, base oblique and cuneate to broadly cuneate or sometimes one side rounded, margin entire, apex caudate-acuminate to obtuse. Inflorescences axillary, less than 30 cm. Flowers 6-7 mm in diam., with 3 bracteoles. Sepals 5, suborbicular, 1-1.5 mm in diam., margin sometimes ciliate. Petals 3-7 mm in diam., concave. Staminal tube globose, glabrous; anthers 5 or 6, oblong. Ovary 3-locular, with thick trichomes. Capsule spherical-pyriform to nearly ovoid, 2-2.5 × 2.5-3 cm, orangish when mature. Seeds grayish brown, oblate, 1.3-1.5 × 1-1.2 cm. Fl. May-Sep, fr. Oct-Apr.
A medium sized tree. It grows 20 m tall. The trunk can be 70 cm across. The young leaves are red. The leaflets are narrowly oblong and unequal on the sides. The flowers are yellow to bronze and waxy. The fruit are 2-4 cm across and pink or red. The seeds have an orange oily aril or fleshy layer.
UsesThe timber is used in house construction in New Guinea and Thailand and is suitable for furniture. In India, a commercially valuable oil for soapmaking is extracted from the seeds (43.5% by weight) and this, like the bark, has some medicinal value, the latter in a liniment used in the treatment of rheumatism. In the Moluccas (Central Halmahera), the mashed leaves in a water solution are sprayed on fruiting heads of rice against disease (De Vogel 4363) and recent research in China and Bangladesh has shown extracts from twigs, bark, fruits and seeds to be efficacious antifeedants, deterring a range of insect pests.
More
The ripe fruit are eaten. The young fruit are used as a vegetable. The fruit are pickled.