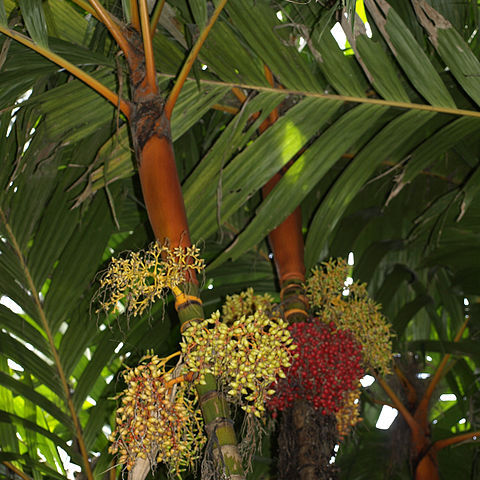
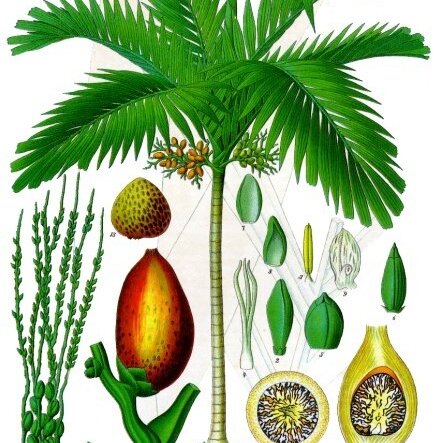
Stems solitary or clustered, tall to short or subterranean, ringed with conspicuous leaf scars. Leaves 4-12, pinnate or occasionally undivided; leaf sheaths closed, forming a distinct, green or yellowish crownshaft, rarely sheaths open and not forming crownshafts; rachis sometimes strongly recurved, mostly spreading horizontally; pinnae usually regularly arranged, spreading in same plane, those at apex joined with only short splits at apices, giving compound pinnae with lobed apices. Inflorescences branched to 3 orders, borne below crownshaft; prophyll present, peduncular bract absent; flowers unisexual, borne in triads of a central large female flower and 2 lateral much smaller male flowers, usually triads only at bases of rachillae, above male flowers only. Fruits usually bright red, small to moderate, ellipsoid to globose or spindle-shaped, commonly beaked, 1-seeded; endosperm ruminate; germination adjacent; eophylls bifid.