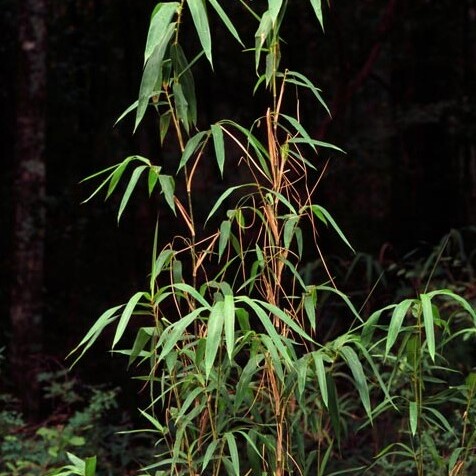
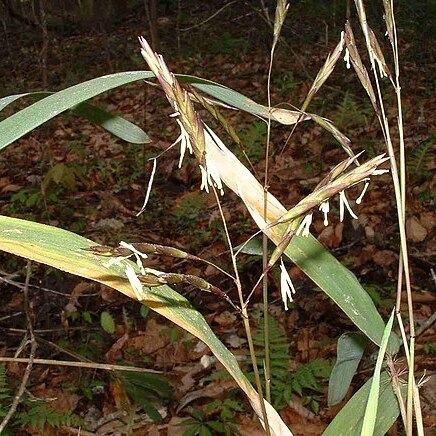
Shrubby or tree-like bamboos with woody culms. Leaf-blades finally disarticulating from the sheath. Inflorescence variable, paniculate or racemose. Spikelets 1–many-flowered, all hermaphrodite or the uppermost reduced, cylindric or ± compressed, often large, loose and linear; rhachilla disarticulating below each floret; glumes 2, persistent, membranous to herbaceous, few-to many-nerved; lemmas usually larger and exceeding the glumes, rounded on the back, herbaceous, becoming chartaceous or coriaceous, 5–13-nerved usually with transverse veinlets, obtuse, acute or acuminate; palea several-nerved, 2-keeled; lodicules 3; stamens 3; stigmas 2–3.
Spikelets many-fld, elongate, the rachilla disarticulating between the lemmas; glumes unequal, distant, shorter than the lemmas, these lanceolate, 11–17-veined, about equaling the 2-keeled paleas; lodicules 3, relatively well developed; stamens 3; stigmas 3; woody perennials with slender, hollow culms, freely branched after the first year; lvs linear or lanceolate, with evident cross-veins, tapering to a petiole and articulated with the sheath; spikelets large, in loose racemes or panicles. 150 (depending on generic circumscription), warm reg.
Spikelets pedicelled, 1–several-flowered, all hermaphrodite or often the uppermost one reduced, linear in outline, cylindrical or laterally compressed, usually somewhat loose; rhachilla disarticulating between the florets, with the joints thickened towards the apex.
Lemmas large, membranous, chartaceous or coriaceous, dorsally rounded, 5-13-nerved, usually with transverse veinlets, with the apex acute, acuminate or mucronate.
Caryopsis narrowly oblong in outline, indurate, dorsally rounded, ventrally with a longitudinal furrow; scutellum circular.
Palea several-nerved, 2-keeled, only little shorter than the lemma, often ciliate along the keels, embraced by the lemma.
Glumes 2 (more rarely 1), slightly unequal, much shorter than the florets, persistent, few-to many-nerved, membranous.
Leaves usually with tessellate venation; laminae finally disarticulating from the sheaths.
Lodicules 3, relatively large, ovate-lanceolate, ciliate, with nerves in the lower part.
Inflorescence terminal and/or lateral, variable, paniculate or racemose.
Ovary sub-globular; styles 2 or rarely 3.
Culms woody with many prominent nodes.
Shrubby or tree-like bamboos.
Stamens 3 (very rarely 6).