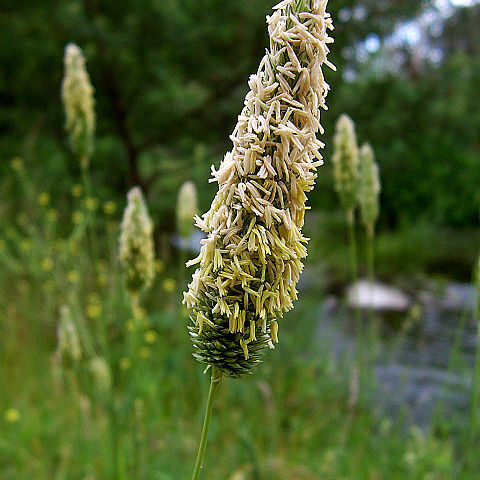
Annual or perennial herbs, or tall woody bamboos. Flowering stems (culms) jointed, internodes hollow or solid; branches arising singly from nodes and subtended by a leaf sheath and 2-keeled prophyll, often fascicled in bamboos. Leaves arranged alternately in 2 ranks, differentiated into sheath, blade, and an adaxial erect appendage at sheath/blade junction (ligule); leaf sheath surrounding and supporting culm-internode, split to base or infrequently tubular with partially or completely fused margins, modified with reduced blade in bamboos (culm sheaths); leaf blades divergent, usually long, narrow and flat, but varying from inrolled and filiform to ovate, veins parallel, sometimes with cross-connecting veinlets (especially in bamboos); ligule membranous or a line of hairs. Inflorescence terminal or axillary, an open, contracted, or spikelike panicle, or composed of lax to spikelike racemes arranged along an elongate central axis, or digitate, paired, or occasionally solitary; axillary inflorescences often many, subtended by spatheoles (specialized bladeless leaf sheaths) and gathered into a leafy compound panicle; spikelets often aggregated into complex clusters in bamboos. Spikelets composed of distichous bracts arranged along a slender axis (rachilla); typically 2 lowest bracts (glumes) empty, subtending 1 to many florets; glumes often poorly differentiated from accompanying bracts in bamboos. Florets composed of 2 opposing bracts enclosing a single small flower, outer bract (lemma) clasping the more delicate, usually 2-keeled inner bract (palea); base of floret often with thickened prolongation articulated with rachilla (callus); lemma often with apical or dorsal bristle (awn), glumes also sometimes awned. Flowers bisexual or unisexual; lodicules (small scales representing perianth) 2, rarely 3 or absent, 3 to many in bamboos, hyaline or fleshy; stamens 3 rarely 1, 2, 6, or more in some bamboos, hypogynous, filaments capillary, anthers versatile; ovary 1-celled, styles (1 or)2(rarely 3), free or united at base, topped by feathery stigmas, exserted from sides or apex of floret. Fruit normally a dry indehiscent caryopsis with thin pericarp firmly adherent to seed, pericarp rarely free, fleshy in some bamboos; embryo small or large; hilum punctate to linear.
Annual or perennial herbs, occasionally shrubs (giant herbs or bamboos), tufted or creeping, sometimes with stolons or rhizomes, usually terrestrial, rarely aquatic. Leaves alternate, distichous (spirally arranged in Micraira), with base completely encircling the node; basal portion a sheath clasping the stem, with margins sometimes extended at the top to form 2 auricles; blade usually linear and tapering, sometimes lanceolate, usually ± flat, occasionally rolled or terete, with parallel veins, generally without a distinct midrib; junction of sheath and blade usually with an adaxial membranous or hairy ligule. Inflorescence a panicle, raceme or spike, or a digitate cluster of racemes or spikes. Basic unit of the inflorescence a spikelet, either sessile or pedicellate and comprising a central axis (rachilla) bearing, alternately in 2 rows: 2 (very rarely 3, 1 or 0) sterile glumes and 1 or more florets, and disarticulating at maturity above and/or below the glumes and often also between the florets. Floret (when complete) comprising a lemma (lower bract), a palea (upper bract) and (between lemma and palea) a flower. Flowers bisexual or unisexual, often both in the same spikelet. Perianth represented by 2 (occasionally 3) minute, membranous or fleshy lodicules. Stamens usually 3; filaments long, slender; anthers 2-celled, versatile. Gynoecium: ovary 1-locular, with 1 anatropous ovule; styles usually 2, rarely 1 or 3; stigmas usually plumose. Fruit a caryopsis (grain) or, very rarely, the pericarp free from the seed. Endosperm starchy.
Leaves solitary at the nodes, sometimes crowded at the base of the stem, alternate and 2-rowed, consisting of sheath, ligule and blade; sheaths encircling the culm, with the margins free and overlapping or ± connate, frequently swollen at the base, the shoulders sometimes extended upwards into triangular auricles; ligule adaxial, placed at the junction of sheath and blade, membranous or reduced to a fringe of hairs, rarely absent (very rarely with a similar abaxial structure—the external ligule); blades usually long and narrow, rarely broad, flat or sometimes rolled or terete, parallel-nerved, rarely with transverse connections, usually passing gradually into the sheath, sometimes amplexicaul or with falcate auricles, rarely narrowed into a false petiole or articulated with the sheath
Spikelets (see pl. tab. 1) usually consisting of 2 (rarely more) glumes and 1 to several lemmas distichously arranged along a rhachilla; each lemma is opposed by a usually thinly membranous palea; enclosed between lemma and palea is the flower (the entire unit is termed a floret); glumes and/or lemmas often awned; florets, and sometimes the entire spikelet, with a basal indurated callus which is either blunt or acute; flower usually hermaphrodite, sometimes unisexual, rather small, consisting of 2-3 minute lodicules (representing the perianth) stamens and ovary; stamens hypogynous, usually 3, sometimes less, rarely 6 or more, with the 2-thecous anthers either opening lengthwise or with a terminal pore; ovary 1-locular; styles 2, rarely 1 or 3; stigmas usually plumose
Spikelets consisting of bracts distichously arranged along a slender axis (rhachilla); the two lower bracts (glumes) empty; the succeeding 1 to many bracts (lemmas) each enclosing a flower and opposed by a hyaline scale (palea), the whole (lemma, palea and flower) termed a floret; base of spikelet or floret sometimes with a horny prolongation downwards (callus); glumes or lemmas often bearing 1 or more stiff bristles (awns); this basic pattern of spikelet structure consistent throughout the family, though often much modified by reduction, suppression or elaboration of parts
Flowers usually bisexual, sometimes unisexual, small and inconspicuous; perianth represented by 2, rarely 3, minute hyaline or fleshy scales (lodicules); stamens hypogynous, 1–6, rarely more, usually 3, with delicate filaments and 2-thecous anthers opening by a longitudinal slit or rarely a terminal pore; ovary 1-locular, with 1 anatropous ovule often adnate to the adaxial side of the carpel; styles usually 2, rarely 1 or 3, generally with plumose stigmas
Inflorescence usually terminal on the culms, rarely axillary, consisting of numerous spikelets arranged in spikes, or in racemes or in a panicle; the spikes or racemes either solitary or more often arranged along a common axis, sometimes digitate, often (Andropogoneae) subtended by a spatheole (sheath without lamina) and often branched, thus forming a complicated pseudo-panicle in which frequently a sessile spikelet is paired with a pedicelled one
Annual or perennial herbs, rarely shrubs or trees, sometimes with rhizomes or stolons; stems erect, ascending or creeping, usually branched at the base, in perennials with sterile shoots and flowering stems (culms) mixed, in annuals only the latter present; culms cylindrical, rarely flattened, jointed, usually hollow in the internodes, closed at the nodes; branches subtended by a leaf, and with a 2-keeled hyaline leaflet (prophyll) at the base
Fruit mostly a caryopsis with thin pericarp adnate to the seed, rarely with free seed, still more rarely a nut or berry; caryopsis commonly combined with various parts of the spikelet, or less often the inflorescence, to form a false fruit; seed with starchy endosperm, an embryo at the base of the abaxial face, and a point or line (hilum) on the base or adaxial face marking the connection between pericarp and seed
Leaf-laminae usually linear or linear-lanceolate, more rarely ovate or oblong, rather narrow, generally parallel-nerved but in a few instances tessellate, expanded, plicate, or sometimes rolled, thus appearing to be terete, often filiform, rarely amplexicaul or with a sagittate base, occasionally with the very base contracted into a pseudo-petiole, very rarely articulated with the sheath
Inflorescence made up of spikelets arranged in a panicle, or in spikes or racemes, these either solitary, digitate, or disposed along a central axis; usually terminal, sometimes (especially in Andro-pogoneae) numerous, each inflorescence being subtended by a bladeless sheath (spatheole) and the whole flowering branch system condensed into a leafy false panicle
Culms usually cylindrical, very seldom compressed, jointed with the nodes solid, the internodes hollow or sometimes solid, erect, ascending or prostrate, sometimes rooting at the nodes, branched or simple; branches at the base with a hyaline 2-keeled prophyll
Leaf-sheaths clasping the culm, usually rather tight, ribbed or smooth, with the margins free or connate to a varying degree and often overlapping, often with a pair of auricles on either side of the mouth
Ligule situated transversely at the junction of sheath and lamina, adaxial, membranous or chartaceous, often reduced to a hairy rim, rarely completely absent in some genera
Leaves solitary, alternate in 2 ranks, all crowded around the base of the stem or/and spaced along the culm, in most cases consisting of sheath, ligule and lamina (tab. 1)
Mostly annual or perennial herbs, rarely shrubs or trees (Bambuseae), often with rhizomes, sometimes stoloniferous
Fruit 1-seeded, usually a caryopsis, with the pericarp adnate to the seed or sometimes free (rarely fleshy)