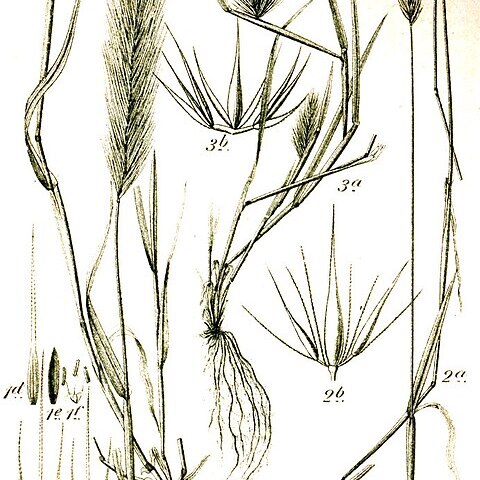
Annuals or perennials, caespitose or culms solitary, bisexual. Leaves: ligule an eciliate membrane; blade rolled in bud. Inflorescence a dense spike-like panicle, with spikelets on contracted axes, with combinations of bisexual and male spikelets or of bisexual and sterile spikelets. Spikelets in triplets, with central spikelet usually sessile and 2 lateral spikelets usually pedicellate, laterally compressed to dorsiventrally compressed, falling with glumes in deciduous triplets or not disarticulating in cultivated forms; central spikelet bisexual with 1 bisexual floret; lateral spikelets sterile or male or rarely bisexual; rachilla usually prolonged beyond bisexual floret, naked. Glumes both on abaxial side of lemma, ±equal or upper glume longer, free, 1 (–3)-nerved, usually awned. Bisexual florets: lemma apically 1-awned, hardened at maturity, not keeled, 5-nerved; stamens 3; ovary hairy. Caryopsis: hilum long-linear.
Spikelets 1(2)-fld, not disarticulating, borne in triads on opposite sides of the rachis, the lateral spikelets often pedicellate and sterile, the central one sessile and fertile; glumes elongate, awned or awn-like, setaceous throughout or widened at base, the 6 in each triad of spikelets forming a false invol to the florets; lemma of the lateral spikelets often reduced or abortive, that of the central spikelet indurate, obscurely veined, its rounded back turned away from the rachis, usually long-awned; rachilla prolonged behind the palea as a short bristle; grasses with mostly flat lvs, scarious, truncate ligules, and dense, bristly spikes which, except in H. vulgare, disarticulate at each joint. (Critesion) 35, widespread