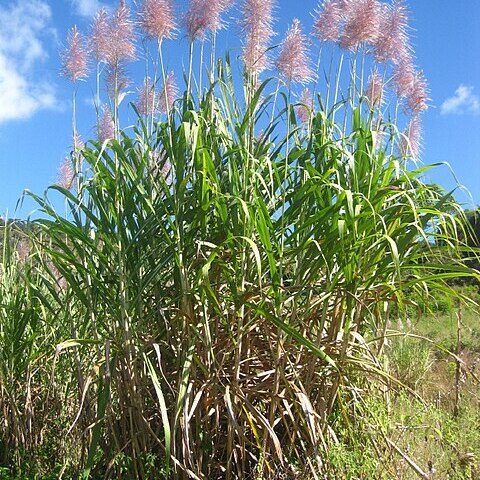
Perennials, often tall; culms solid. Leaf-blades linear; ligule scarious or a line of hairs. Inflorescence large, plumose, often silvery, with many racemes crowded upon the primary panicle-branches; racemes usually flexuous, the rhachis fragile and bearing paired similar spikelets, one sessile, the other pedicelled; internodes linear, slender, usually more than 1/2 the length of the sessile spikelet. Spikelets lanceolate, enveloped in long silky hairs from the callus; callus very short, truncate; glumes equal, membranous or sometimes sub-coriaceous below, the lower flat or rounded on the back; lower floret reduced to a lemma, this lanceolate, shorter than the spikelet, hyaline; upper floret hermaphrodite; lemma lanceolate, hyaline, awnless or with a straight awn, entire or rarely bilobed, sometimes reduced to a subulate vestige; stamens 2–3. Caryopsis subglobose to narrowly oblong.
Spikelets all alike, in pairs, one sessile, the other pedicellate, surrounded at the base by long silky hairs, the rachis readily disarticulating below the spikelets; glumes rather firm, 1-to 3-nerved, acute or acuminate; sterile lemma similar to the glumes but hyaline, the fertile lemma shorter than the glumes, hyaline, awn-less, sometimes wanting.
Inflorescence a panicle, often large and plumose, bearing numerous racemes on its branches; racemes loose, fragile, with slender internodes.
Spikelets alike, paired, one sessile, one pedicelled, lanceolate, enveloped in long silky hairs from the callus.
Superior lemma entire or bidentate, awned or awnless, sometimes almost suppressed; stamens 2–3.
Inferior glume membranous or sometimes subcoriaceous below, flat or rounded on the back.
Inferior floret represented by a short hyaline lemma.