Herbs, perennial, 11-150 cm tall; rhizomes becoming woody; stemless rosettes often present. Stems erect, simple, ribbed, glabrate proximally to sparsely strigillose distally, minutely stipitate glandular below leaves. Leaves cauline, much reduced upward, scabrous, abaxially sparsely minutely stipitate glandular, margin scabrous-ciliate, midvein prominent abaxially, apex acuminate to acute or rounded, mucronate; lowest leaves withered by anthesis, long, slightly winged petiolate (petiole to 30 cm), petiole base sheathing; blade oblanceolate to ovate, (2.1-)30-50 × (0.9-)6-12 cm, base attenuate, margin undulate, coarsely serrate, veins pinnately 6-10-paired; lower to upper leaves shortly petiolate (base sheathing) or sessile, oblanceolate to lanceolate, 2-18 × 0.6-5 cm, base attenuate, margin coarsely serrate to serrulate or entire; synflorescence leaves lanceolate, 1.3-7 × 0.2-1 cm. Capitula (2-)14-50 or more, in terminal corymbiform synflorescences; peduncles 25-65 mm, sparsely strigillose, moderately to densely minutely stipitate glandular; bracts linear-lanceolate, entire, sometimes grading into phyllaries. Involucres campanulate, 7-10(-12) mm; phyllaries 3-seriate, unequal, green along midvein, membranous, base ± hardened, margin erose, ciliate, midvein ± pronounced, slightly translucent; outer phyllaries narrowly lanceolate, 4-5 × 0.8-1 mm, sparsely strigillose, distally sparsely minutely stipitate glandular, sometimes ± leaflike, margin narrowly scarious, apex acute, ciliate, tip purplish; middle phyllaries oblong to lanceolate-oblong, 6-7 × ca. 1 mm, abaxially glabrous to sparsely strigillose distally or along midvein, eglandular or very sparsely glandular, margin scarious, apex acuminate, sometimes mucronate, distal margin and apex purplish; inner phyllaries linear-lanceolate to linear-oblong, 8-10 × 0.6-1 mm, glabrous, sparsely minutely stipitate glandular, margin scarious, apex acuminate, erose, purplish. Ray florets 14-30, blue or pale lavender or to purple, lamina 7-15 × 1.5-2.5 mm, glabrous, eglandular; disk florets yellow, 5-7 mm, limb campanulate, 3.5-4 mm, lobes erect, tip spreading, narrowly triangular, ca. 2 mm, glabrous, eglandular. Achenes dark, obovoid, slightly compressed, 2.5-3 mm, sparsely to moderately strigillose, sparsely minutely stipitate glandular apically, 4-6-ribbed. Pappus 4-seriate, reddish, of barbellate bristles; outermost bristles few, slender, 0.2-0.3 mm; outer bristles slender 1.5-2 mm; inner bristles 4.5-5 mm, tapering; innermost bristles 6-7 mm, slightly clavate. Fl. Jul-Sep, fr. Aug-Oct. 2n = 54.
More
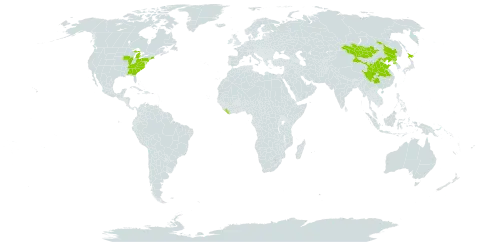
Plants 50–150(–300) cm, densely colonial; rhizomes fleshy, ± woody with age, with abundant fibrous roots. Stems 1–3+, erect, sparsely to densely (distally) strigillose. Leaves basal and cauline, very coarse, margins scabrous, apices mucronate, faces scabrous; basal usually deciduous by flowering; proximal cauline persistent, long-petiolate (petioles ± winged, bases sheathing), blades strongly 1-nerved, oblanceolate, 300–500 × (50–)60–120 mm, bases attenuate, margins undulate, recurved, coarsely serrate, teeth mucronate, apices acuminate, acute, or rounded; mid and distal subpetiolate to sessile, blades oblanceolate to lanceolate, 40–180 × 10–50 mm, bases attenuate to cuneate, sheathing, margins serrate or entire, apices acute to acuminate; distal (arrays) abruptly reduced, lanceolate, 5–10 mm, apices acute to acuminate. Heads 14–50+ in corymbiform arrays, branches ascending. Involucres campanulate, (6.5–)7–10(–12) mm. Phyllaries in 3–4 series, ovate to lanceolate (outer) or linear-lanceolate to linear (inner), green to base along midnerves or outer sometimes largely foliaceous, apices acute (outer) to long-acuminate (inner), abaxial faces glabrous or sparsely strigillose. Rays 14–30; laminae pale lavender or purple, 10–15 × 1.5–2.5 mm. Disc florets (20–)25–30(–50); corollas light yellow turning lavender at least in lobes, (4.5–)5–6 mm, tubes about as long as campanulate throats. Cypselae light brown, linear-obconic, slightly compressed or plump, 1.5–2 mm, nerves 4–5(–6), faces glabrate to thinly strigillose; pappi white or cream-colored, 6–8 mm, shorter than disc corollas. 2n = 54.
Coarse, rough-hairy plants, 5–20 dm from a stout caudex; lower lvs long-petiolate, with large, elliptic, conspicuously toothed blade 8–40 × 2.5–15 cm, the middle and upper smaller, sessile or nearly so, and mostly entire; infl corymbiform, flat-topped; invol 7–10 mm, strigose-puberulent or subglabrous, its bracts not much imbricate, the larger ones mostly 1–2 mm wide; rays 15–20, purple or blue, 1–2 cm; 2n=54. Native of s. Siberia, casually escaped from cult. in e. U.S.
A tall herb. It keeps growing from year to year. It is 1.5-2 m tall and spreads 1-1.2 m wide. The stem has a thickened base. The leaves have long stalks. They are rough and hairy. They are narrowly oval and 40 cm long. There are teeth around the edge. The daisy like flowers are in flat topped arrangements. They are purple to blue.
Can be grown by cuttings, divisions or seedlings. Seeds needs stratification.