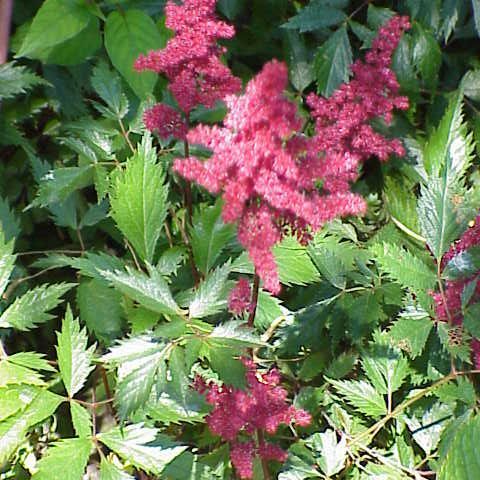
Herbs, clump-forming, not rhizomatous, not stoloniferous; caudex stout. Flowering stems erect, leafy, 150-200 cm, stipitate-glandular with unicellular and multicellular hairs. Leaves basal and cauline, usually ternately decompound or 3-pinnately compound, never simple, leaflets short-petiolulate; stipules present; petiole present, glandular-stipitate, hairs uniseriate and multiseriate; leaflet blades ovate, largest terminal leaflet usually 3-lobed, base of leaflet oblique, truncate, or cordate, margins coarsely and irregularly double-serrate, teeth mucronate, apex acuminate, surfaces short stipitate-glandular on veins abaxially, glabrous adaxially; venation of terminal leaflet pinnately-palmately netted. Inflorescences relatively large, plumose panicles, rarely congested and spikelike, terminal from terminal bud of caudex, (branched), 500-2000-flowered, bracteate, (elongate-triangular); (branches stipitate-glandular). Flowers usually unisexual, rarely bisexual, plants usually dioecious, rarely polygamous, (becoming reflexed in fruit, short-pedicellate); hypanthium 1/4 adnate to ovary proximally, free from ovary 1 mm, (shallow), greenish whitish; sepals 5, white [pink or red to purplish]; petals absent or (1-)5, white [pink or red to purplish]; staminate flowers: stamens 8-10, (erect), inserted below rim of hypanthium, filaments filiform, (anthers cordate-orbiculate), ovary abortive, surrounded by distinct nectary disc; pistillate flowers: stamens abortive, pistils 2(-3)-carpellate, carpels connate proximally, ovary superior, barely adnate proximally to hypanthium, 2-or 3-locular, with poorly differentiated nectary disc, placentation axile, styles 2(-3), stigmas 2(-3), capitate. Capsules 2(-3)-beaked. Seeds brown, winged due to presence of loose seed coat, often twisted at both ends, oblong-cylindric, striate or lightly wrinkled, lustrous. x = 7.
More
Herbs perennial. Rhizomes thick. Stems brown paleaceous hairy or long pilose. Leaves alternate, long petiolate, 2-4 × ternately compound, rarely simple; stipules membranous; leaflets lanceolate, ovate, or broadly ovate to elliptic, margin dentate. Inflorescence a terminal panicle, bracteate. Flowers white, lilac, or purple, bisexual or unisexual, rarely plants polygamous or dioecious. Sepals (4 or)5. Petals usually 1-5, sometimes more or absent. Stamens usually (5 or)8-10. Carpels 2(or 3), ± connate or free; ovary subsuperior or semi-inferior, 2(or 3)-loculed with axile placentation or 1-loculed with marginal placentation; ovules many. Fruit a capsule or follicle. Seeds small.
Polygamo-dioecious; fls regular, 5-merous; hypanthium saucer-shaped; pet narrow; stamens 10; ovary superior; carpels 2(3), ± connate (except the styles) and with axile placentas, separating into erect follicles at maturity; tall perennial herbs with large, alternate, decompound lvs and large panicles of small, white or yellowish fls. 25, N. Amer., e. Asia.