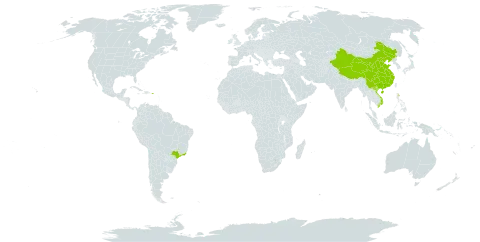
Culms 10–18 m, 4–7 cm in diam., basally slightly flexuose, apically suberect or slightly drooping; internodes 25–35 cm, sometimes several at base with pale yellow stripes, initially thinly white powdery, usually glabrous; wall thick; basal nodes sometimes with short aerial roots; branching to base. Branches solitary at basal nodes, 3 to several at higher nodes, with central 3 dominant; branchlets at lower nodes usually condensed into tough or weak thorns. Culm sheaths deciduous, leathery, subglabrous or inconspicuously strigose, apex asymmetrical, arched-concave; auricles unequal, usually wrinkled; larger auricle oblong to oblanceolate, 4–5 mm wide; smaller auricle ovate to elliptic, 3–4 mm wide; oral setae undulate; ligule 5–7 mm, dentate, laciniate, shortly white fimbriate; blade erect, ovate-triangular to ovate-lanceolate, base nearly 1/2–3/5 width of sheath apex, abaxially glabrous, adaxially stiffly dark brown hairy, margins with undulate setae near base. Leaf blade linear-lanceolate to lanceolate, 7–18 × 1–1.8 cm, abaxially sparsely pubescent, adaxially glabrous. Flowering branches with pseudospikelets solitary or clustered at each node, lanceolate, ca. 3 cm, compressed; prophylls 2-keeled; gemmiferous bracts usually 2, ovate, apex obtuse; fertile florets 4 or 5, apical 2 to several florets sterile; rachilla segments 2–3 mm, apex inflated and ciliate. Glumes 1 or sometimes absent, similar to lemma but shorter; lemma lanceolate, to 1.2 cm, base glabrous, veins inconspicuous, base rounded or broadly cuneate, margins ciliolate near apex, apex obtuse or acute with a subulate tip; palea keels strongly folded near apex, ciliolate or scabrous, 5-veined between keels, apex usually penicillate; lodicules 3, subequal, ovate or obovate, margins long ciliate. Filaments distinct; anthers apex obtuse, slightly concave. Ovary obovoid or ovoid, stalked, apex thickened and strigose; style solitary, very short, hairy; stigmas 3. New shoots Jul–Aug, fl. Mar–Apr.