Clumps rather open. Culms 8–15 m, 5–9 cm in diam., basally straight or flexuose, apically drooping; internodes deep green, 20–30 cm, initially thinly white powdery, stiffly pale brown strigose; wall slightly thick; nodes slightly prominent, basal several with aerial roots and rings of grayish white silky hairs below and above sheath scar; usually branching from lower nodes. Branches several to many, clustered, central dominant. Culm sheaths deciduous, ribbed-striate when dry, densely stiffly deciduously dark brown hairy, apex arched below blade, concave below auricles; auricles conspicuous, ascending, nearly equal in shape and size, oblong or reniform, 8–10 mm; oral setae curved, fine; ligule 3–4 mm, serrate, very shortly white ciliolate; blade deciduous, erect or deflexed, broadly triangular to triangular, base slightly rounded, ca. 1/2 width of sheath apex, abaxially sparsely stiffly dull brown hairy, adaxially densely stiffly dull brown hairy between veins, apex involute, sharply apiculate. Leaf blade narrowly lanceolate, 10–30 × 1.3–2.5 cm, both surfaces glabrous. Pseudospikelets several, clustered at nodes, narrowly lanceolate to linear-lanceolate, slightly flattened, 2–3.5 × 0.4–0.5 cm, apparently bifid; gemmiferous bracts several; florets 5–10; rachilla segments 1.5–3 mm. Glumes 1 or 2, abaxially shortly hairy near apex, apex apiculate; lemma 8–10 mm, abaxially shortly hairy near apex, apex apiculate; palea slightly shorter than lemma, keels ciliolate; lodicules 3, 2–2.5 mm, margins long ciliate. Anthers ca. 6 mm, apex penicillate. Style 3–7 mm, slender; stigmas 3, short.
More
An erect clump forming spineless bamboo. It is a large bamboo with strong stalks used for buildings. The stalks can be 20 m tall and 5-10 cm across at the base. They are often not straight. The stalks can be green and glossy or yellow or yellow with green stripes. It very rarely flowers. The distinctive culm sheath (top of the leaf that is wrapped around the stalk) helps identify the plant. The culm sheath is triangular and 15-45 cm long by 20 cm wide. The edges are hairy. The leaf blade is 6-30 cm long by 1-4 cm wide. The stems are smooth and usually yellow green and smaller than Kauayan-tinik of the Philippines and with a thinner wall.
Culms 6-10 m. high, erect, as much as 10 cm. in diameter, at first green but finally turning yellow; sheaths (of the branches) crowded, keeled, auriculate; blades lanceolate-acuminate, rounded at the base, mostly 15-30 cm. long, 1.5-4 cm. wide, the petioles rather broad, 3-5 mm. long; spikelets 1.5 cm. long, about 6-flowered; lemmas 8-10 mm. long, acute or awn-pointed.
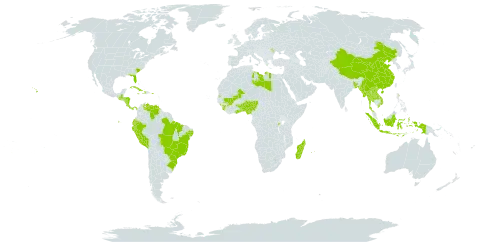
A tropical plant. It grows throughout the tropics and subtropics. It grows up to 1,200 m altitude. It does best at low altitudes. It can stand frost down to-3°C. It has been introduced to PNG and is common in the lowlands. (A different large bamboo is grown and eaten in the highlands of Papua New Guinea.) In the Cairns Botanical Gardens. In XTBG Yunnan. It suits hardiness zones 9-12.
More
Riversides and open forests in Yunnan.