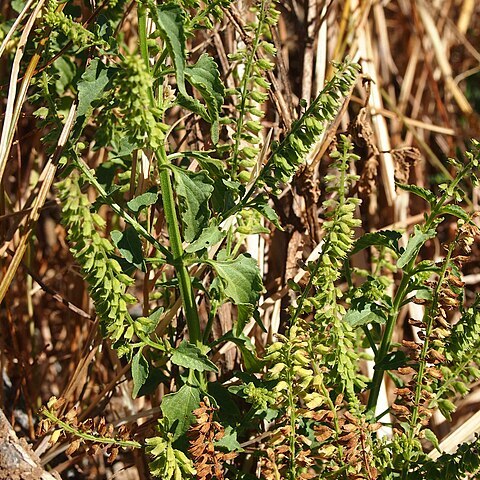
Erect herb, 0.4-1 m. Stem much branched, ± glabrous, prominently 4-angled. Leaves thin-membranaceous, ovate to oblong-ovate, 2-5 by 1-3.5 cm, acuminate or caudate, base acute or attenuate, irregularly serrate, glabrous on both surfaces; petiole slender, 1-4 cm. Raceme-like inflorescence 3-6 cm long (in fruit over 10 cm). Bracts minute, lanceolate, aristate, 1-2 mm. Pedicels 1-2 mm, persistent. Calyx campanulate, pubescent, 1.5-2 mm long (in fruit 3-3.5 mm, slightly inflated at base); upper lip broad, entire, reflexed; lower lip 4-toothed, 2 lateral teeth ovate, and 2 lower teeth cuspidate. Corolla pale lilac to purple or flesh-coloured, sometimes white, 2-2.5 mm long. Stamens 4, in 2 pairs, included. Nutlets minute, broadly ellipsoid, compressed, smooth.
Freely branched, glabrous herb, 0.3-0.5 m tall; stems 4-angled. Leaves petiolate; blade ovate, 20-50 x 10-35 mm, under-surface freely gland-dotted, apex acuminate, base cuneate to obtuse, entire, upper margin crenate-dentate; petiole slender, 20-30 mm long. Inflorescence lax to fairly dense, 50-100 x 8 mm; bracts minute, ovate; pedicels 1-2 mm long. Calyx glandular-puberulous, 1.25 mm long at flowering, enlarging to 3 mm long. Corolla white or mauve, 1.5-2 mm long. Stamens scarcely exserted; lower pair attached at the corolla throat, the upper pair about the middle of the tube.
A small herb. It grows 90 cm high and spreads 50 cm wide. The stem is erect and branching. The leaves are oval or sword shaped and opposite. They are green and 5 cm long. The flowers are tube shaped and white. They have 2 expanding lips. They grow in groups along one side of a stalk.