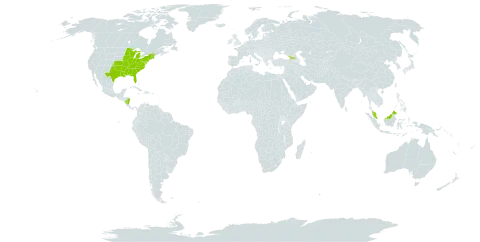
Tree to 30 m, the brown bark exfoliating in thin layers, scaly-roughened on larger trunks; lvs ovate-oblong or deltoid-ovate, 4–8 cm, acute, sharply double-serrate above, entire toward the cuneate base, tomentose beneath when young, soon glabrescent on the surface but remaining softly villous on the veins beneath and tomentose on the petiole; lateral veins 6–10 pairs; fruiting catkins on peduncles 5–8 mm, cylindric, 1.5–3 cm; scales pubescent, 6–8 mm, parted above the middle into 3 oblong lobes; frs pubescent, depressed-ovate, 3–4 × 4–7 mm, the body 2.5–4 mm wide. Swamps and flood-plain forests; N.H. to Fla., w. to s. O., se. Minn., e. Kans. and Tex.
A deciduous tree. It grows 9-30 m high. It forks about 3-6 m above the ground to form a broad crown. The bark is dark and furrowed in older trees. The leaves are triangular with irregular teeth along the edge. They are 10 cm long. They taper at the base and are pointed to the tip. There are hairs on the veins underneath. The male and female flowers are on catkins on the same tree. Male catkins are 7.5 cm long and yellow-brown and hang down. Female catkins are green and upright. The fruit is a catkin which breaks up when ripe.