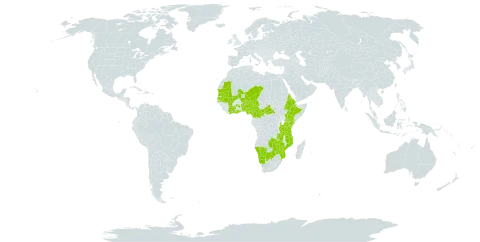
A medium sized tree. It can grow to 15 m high. It loses its leaves during the year. The bark is dark grey, rough and flaky. The leaves are alternate, long and narrow. They are 7-15 cm long by 1.5-2.5 cm wide. They are dull green and leathery. They remain finely hairy underneath. They taper to both ends. The flowers do not have petals. The stamens are yellowish-green. The fruit is round and 2 cm across. They are smooth and yellow when ripe. They have 1-3 seeds. The seeds are brown and 1 cm across.
Leaf-lamina 4–15 x 0.8–4.5 cm., linear, linear-lanceolate, narrowly elliptic, oblanceolate or oblong, apiculate, long-acuminate, acute or more rarely blunt at the apex, cuneate at the base, pubescent or scaberulous above, often glabrescent later, more persistently pubescent below; midrib prominent below; petiole up to 1.5 cm. long, pubescent.
Inflorescence of axillary racemes, 2–4 cm. long, often flowering at about the time of leaf-fall or sometimes a little later; peduncles very short, 2–5 mm. long, densely pubescent; pedicels 2–5 mm. long, densely pubescent; bracteoles c. 1 mm. long, subulate, densely pubescent, entire or with two side teeth.
Sepals greenish-yellow, c. 3 x 1.7 mm., reflexed at maturity, oblong-lanceolate to narrowly ovate, acute at the apex, pubescent within, densely velvety-pubescent outside, densely ciliate at the margins; receptacle 4-sided, papillose-fimbriate.
Ovary ovoid, glabrous, with about 10 ovules on 2 placentas; style c. 0.6 mm. long; stigma small, not much wider than the style.
Deciduous tree up to 15 m. tall, but often much less; bark dark grey, rough and flaking; young branches densely pubescent.
Seeds brown, c. 1 cm. in diam., globose or somewhat compressed, rugose, embedded in a fleshy pulp.
Fruit c. 1.7 cm. in diam., globose, almost smooth, yellowish, with a minute apiculus, 1–3-seeded.
Stamens 6–14 with glabrous filaments 6–7 mm. long.
Savannah tree, up to 40 ft. high
Gynophore 4 mm. long, glabrous.
Graceful drooping foliage.