Leaves 8–35 cm long; petioles 3–12 mm long including a 2–7 mm long pulvinus; rachis deeply canaliculate with raised and winged margins, glabrous or pubescent; leaflets in 15–30 overlapping or widely spaced pairs, middle leaflets or those next to the proximal largest; proximal leaflet pairs 1.5–4.5 × 0.5–1.5 cm, the middle ones 3–6.5 × (0.5)0.7–1.8 cm, the distal ones 2–5 × 0.5–1.5 cm, oblong or oblong-elliptic, rounded, obtuse, retuse or emarginate at the apex, obliquely round or cordate at the base, glabrous or pubescent; midvein central or subcentral, with 3–5 secondary veins diverging from the proximal leaflet base.
A tree. It grows 15 m tall. The bark is cracked. It is dark grey. The leaves are 8-35 cm long. The leaflets are in 15-30 overlapping pairs. The leaflets near the middle are largest. The flowers are in branched groups near the ends of branches. The fruit are pods 7-25 cm long by 3-5.5 cm wide. They are oblong and dark brown. There are up to 6 seeds. These are 15-25 mm long by 12-16 mm wide. They are oval.
Stipules persistent, 15–55 × 1–3 mm, filiform, linear, lanceolate or spathulate; auricles 10–20 × 5–10 mm, reniform to subcircular, caducous independently of the stipules, lamina palmately nerved, pubescent.
Tree up to 15 m tall; bark deeply or shallowly fissured longitudinally and often coarsely reticulate, flaking in thick irregular scales, dark grey; young branchlets glabrous or brown-pubescent.
Sepals 4–5, the proximal median sometimes fused with one or both of the laterals, 3–4 × 1.5–3 mm, oblong, orbicular or oblong-lanceolate, imbricate, entire to densely ciliate on the margins.
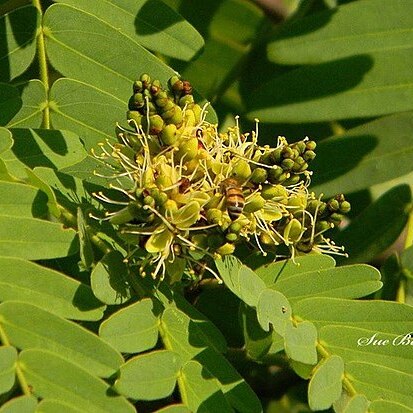
Inflorescences in much-branched terminal and/or axillary panicles up to 10 cm long; bracts 2–3.5 × 2–3 mm, ovate to oblong, acute at the apex.
Pods 7–25 × 3–5.5 cm, oblong to obovate, round to obtuse at the apex, dark brown, with spreading, suberect or revolute ventral flanges.
Flowers 5–8 × 3–4 mm; pedicels to 3 mm long; bracteoles 6–8 × 3–5 mm, obovate or orbicular, densely pubescent.
Ovary 3–6 × 2–3 mm, to 8-ovulate, densely pubescent; stipe to 4 mm long.
Stamens 10, united to 1 mm at the base; filaments 10–12 mm long.
Petals 0–3, 3–5 × 0.5–1 mm, filiform to spathulate.
Seeds up to 6, 15–25 × 12–16 mm, oblong to ovoid.
Dormant axillary buds much flattened.