Shrub or small tree, 0.3-10 m, up to 10 cm ø. Leaves 20-50 cm long; leaflets 3-15, ovate-oblong to ovate-lanceolate, sparsely hairy above, more or less pubescent beneath, sometimes completely glabrous, 3.5-11 by 1.5-5 cm, the younger ones usually densely pubescent; petiole 5-10 cm, lateral petiolules 2-9 mm, terminal one 3-40 mm. Peduncle almost absent, rachis 7-60 cm. Bracts deltoid, small. Flowers greenish-white to greenish-red or purple. Male: Pedicels very slender, up to c. 3 mm long, sepals pubescent, sometimes toothed, c. 0.5-1 by ⅓-½ mm; petals sparsely pubescent to nearly glabrous, sometimes toothed, 1-2 by 0.5-1 mm; filaments subulate, c. 0.6 mm, anthers c. 0.4 mm long. Female: Pedicels up to 2.5 mm, sepals and petals as in male; stamens 0 or vestigial. Mature dried drupes 1-4 together, 4-5(-7) mm long, pedicels 2-6 mm.
Shrub or tree to 10 m high, dioecious or bisexual. Leaflets 3–15, usually 5–7, ovate-oblong to ovate-lanceolate, acuminate to 13 cm long, serrate, each serration with an abaxial, marginal gland terminating a lateral vein, glabrous or sparsely pubescent or velutinous; base oblique. Inflorescence raceme-like, to 60 cm long. Sepals pubescent, to 1 mm long. Petals 1–2 mm long, green-white to green-red or green-purple. Stamens c. 1 mm long. Drupelets 1–4 together, each ovoid or ellipsoidal, 4–10 mm long, slightly 2-ribbed.
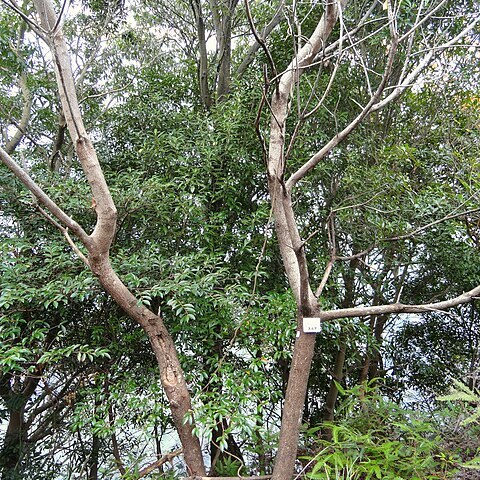
An evergreen shrub. It grows to a height of 3-7 m and spreads to 3 m across. The stem is erect and branching. It is hairy when young. The leaves are compound leaves and produced alternately. They are 30-50 cm long and have 5 to 11 leaflets. These are oval but tapering to the tip and with coarse teeth around the edge. The leaflets are 5-8 cm long by 2-4 cm wide. The flowers are purple and small. The fruit are about 5 mm long.