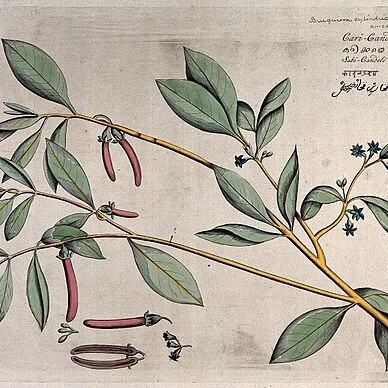
Trees 10-15 m tall, d.b.h. 15-25 cm. Bark gray, smooth, with few lenticels. Stipules 2.5-3.5 cm. Petiole 1-3.5 cm; leaf blade elliptic, 7-17 × 2-8 cm, thin, secondary veins abaxially remote and thin, reticulate veins mostly obscure, base cuneate, apex acute. Cymes pedunculate, 2-or 3-flowered. Pedicel 1-4 mm. Flowers greenish, less than 2 cm. Calyx tube 4-6 × ca. 2 mm, not ribbed, smooth; lobes 7 or 8, ± as long as tube. Petals white but soon turning brown, 3-4 mm, 2-lobed, outer margins usually basally fringed with white hairs. Stamens 1.5-2.5 mm. Disk in open flowers not entirely lining calyx tube. Style 3-4 mm. Fruiting calyx tube ca. 1 cm, slightly ribbed; lobes recurved. Hypocotyl cylindric, often curved, 8-15 × ca. 0.5 cm. Fl. autumn, fr. winter-spring (and sporadically year-round).
Tree up to 23 m by 20-30 cm, buttresses small, up to 1 m. Bark grey, with a few small, corky lenticels. Leaves thin, elliptic, 7-17 by 2-8 cm, acute, base cuneate; nerves c. 7 pairs, distinct, rarely obscure on both surfaces; petiole 1-4.5 cm. Stipules 2½-3½ cm long. Cymes 3-flowered. Peduncle 6-8 mm. Flowers greenish, at anthesis 10-12 mm long. Pedicels 1-4 mm. Calyx tube smooth, 4-6 by 2 mm, lobes 8, about as long as the tube. Petals 3-4 mm long, the lobes c. 1/6 as long as the petal, with 2 or 3 bristles at the apex, outer margins usually fringed with white hairs in the lower part. Stamens 1½-2½ mm long, anthers oblong, 0.5 mm long, slightly apiculate. Calyx tube in fruit 10-12 mm long, the lobes reflexed, not accrescent. Hypocotyl cylindric, often curved, 8-15 cm by 5 mm.
Tree to 20 m high with small stilt roots at base; knee roots abundant; bark grey. Leaves elliptic, acute, not leathery; lamina 5–17 cm long, 2.5–8 cm wide; petiole 1–4.5 cm long; stipules 2.5–3.5 cm long. Inflorescence 3-flowered; peduncle c. 5 mm long; pedicels c. 2 mm long; flowers cream to green. Hypanthium 4–6 mm long, 2 mm wide. Sepals usually 8, at least half as long as hypanthium, reflexed in fruit. Petals 3–4 mm long, sparsely hairy along margins; lobes c. 0.5 mm long; apical bristles much longer than lobes. Anthers 0.5 mm long, shorter than filaments, tapering upwards. Fruit 10–12 mm long. Hypocotyl 8–15 cm long, c. 5 mm wide, usually curved, not ribbed.