Vines, woody, twining or trailing, to 2 m. Stems slender, ± pubescent. Leaves pinnately 3-foliolate; stipules small, ovate, hairy, usually deciduous; petiole 1-2 cm; stipels absent; petiolules extremely short; leaflets papery or nearly leathery, with glandular spots, sparsely pubescent on both surfaces, denser abaxially, basal veins 3, obviously convex below; terminal leaflet elliptic or obovate-elliptic to obovate, 1.2-4 × 0.8-1.5(-3) cm, apex obtuse or rounded; lateral leaflets smaller, obliquely elliptic to obliquely obovate. Raceme axillary, usually less than 2 cm, 1-5-flowered; peduncle 2-5 mm, densely brown to dull brown villous. Calyx campanulate, 5-lobed, or 4-lobed with upper 2 incompletely connate; lobes linear-lanceolate. Corolla yellow, ca. 1 cm, usually deciduous; standard obovate, with emarginate auricle and claw at base; wings narrowly elliptic, slightly curved, base auriculate; keels curved at apex, densely very pale brown villous. Ovules several. Legume oblong, 1.5-2.5 × 0.4-0.6 cm, leathery, densely villous, transversely constricted between seeds. Seeds 2-7, dark brown, ellipsoidal, ca. 4 mm; strophiole convex. Fl. Sep-Nov, fr. Oct-Dec.
More
A slender trailing herb. The root is woody. The stems have a rusty red covering of hairs. The leaves are divided into 3 leaflets. The leaflets are oval. The leaflets are 1-7 cm long by 1-3 cm wide. They are covered with dense grey hairs. The flowers are in clusters of 2-6. They are yellow and crimson. They are on a short stalk in the axils of leaves. The fruit is a pod 1.5-2.5 cm long by 5-7 mm wide. It is covered with fine silky hairs. There are grooves across the pod between the seeds. There are 3-6 seeds.
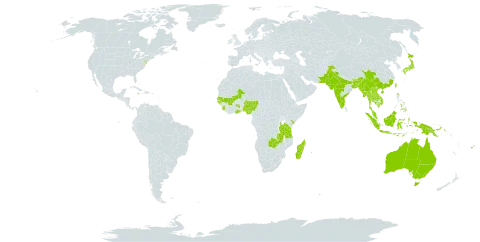
It is a tropical plant. It grows in Nepal to 1000 m altitude. It is drought resistant. It grows in hedges and open forests. In southern China it grows between 100-1,500 m above sea level. in Sichuan and Yunnan.
More
Fields, roadsides, grassy slopes, seasides; at elevations from 100-1,500 metres. Open grassland, dry scrub and deciduous monsoon forests. It also occurs on ridges between cultivated fields and along roadsides.