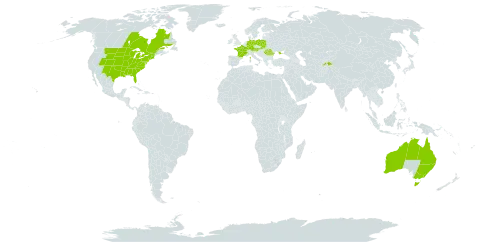
Shrub or tree to c. 25 m high, deciduous. Leaves: lamina ovate-lanceolate to broadly ovate, oblique, 4–14 cm long, mostly 3–7 cm wide, rounded and asymmetric at base, serrate margin, acuminate at apex, glabrous to scabrous above, (glabrous to) pubescent below, somewhat 3-veined; petiole 6–12 (–20) mm long; stipules lanceolate, c. 1 cm long. Inflorescence few-flowered. Bisexual flowers usually solitary; perianth lobes linear-oblong, c. 3 mm long; stamens equal to or slightly longer than perianth; ovary ovoid-cylindrical, c. 4 mm long; stigmatic arms recurved. Drupe ellipsoidal or globose, 7–13 mm long, orange to red to purple to ± black; pedicel 0.7–2 cm long. See also Walsh (2015).