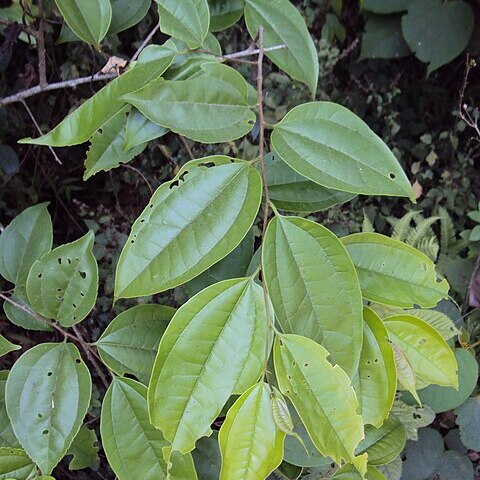
Trees, to 20 m tall, evergreen. Bark grayish white, gray, or grayish brown. Branchlets golden brown pubescent when young, brown and glabrescent with age, with scattered short linear lenticels. Winter buds brown, ca. 2 mm; scales at least inner ones pubescent. Stipules linear-lanceolate to linear, 2-7 mm, not enclosing bud, caducous. Petiole 3-12 mm, pubescent, glabrescent; leaf blade usually golden brown pubescent when young, ovate-elliptic to ovate-oblong, 5-15 × 2.5-7.5 cm, ± coriaceous, base broadly cuneate to ± rounded and distinctly asymmetric, margin entire or weakly serrate above middle and with 15 low rounded teeth on each side, apex acuminate to caudate-acuminate; secondary veins 1 or 2 on each side of midvein. Inflorescence a branched cyme, ca. 10-flowered, golden brown pubescent when young; proximal inflorescences with male flowers, distal inflorescences with male and female flowers. Styles 2, linear, undivided. Infructescences branched, 2-3.5 cm, pubescent or glabrous, with 3 or 4 drupes and several prominent scars from fallen flowers. Drupe yellow, becoming red to orange-red when mature, broadly ovoid, 7-9 mm, base rounded, apex conic-acute. Stone white, ovoid, ca. 6 mm, reticulately foveolate, conspicuously 4-ribbed.
Tree to 25 m high; young branchlets rufous-pubescent, glabrescent. Leaves: lamina ovate to oblong, 5–13 cm long, c. 3–4.5 cm wide, obtuse or rounded to subcordate at base, oblique, serrulate towards apex, acuminate, strongly 3-veined, pubescent on veins beneath; petiole 3–10 mm long; stipules ovate. Inflorescence to 3 cm long, woolly hairy; bisexual inflorescences c. 2–7-flowered, lax; male inflorescences c. (5–) 10–20-flowered, much-branched. Perianth lobes 4 or 5, oblong, c. 2 mm long, obtuse, membranous, ciliate. Stamens 4 or 5; anthers large, sometimes absent. Receptacle woolly. Ovary ovoid, c. 2 mm long; stigmatic arms linear, spreading, absent in male flowers. Drupe ovoid, somewhat compressed, 7–11 mm long, red or black, glabrous; beak bifid; pyrene rugose. See also Zich et al. (2020).