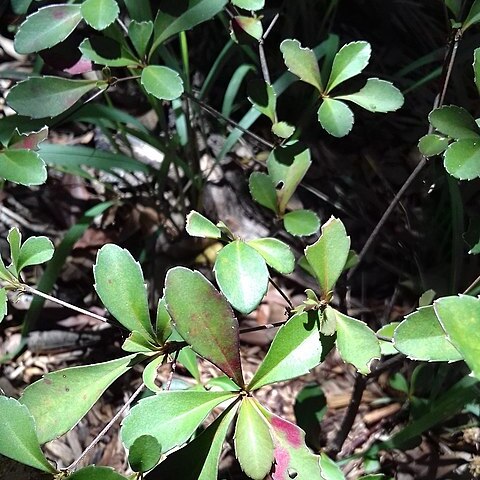
Trees or shrubs; monoecious or dioecious; with indumentum of simple hairs. Leaves alternate, petiolate, stipulate; blades usually dentate, pinnately veined, often with glandular spots at the base. Inflorescences axillary, thyrsoid or racemi-form; bracts eglandular. Staminate flowers more or less pedicellate; calyx splitting at anthesis into 3 or 4 valvate lobes; petals and disc absent; stamens numerous (35-80), densely crowded on a convex receptacle, the anthers 4-loculate, connective more or less ap-pendaged; pollen grains subglobose, 3-colporate, tectate, psilate; pistillode absent. Pistillate flowers pedicellate; calyx-lobes 3-6, imbricate; disc and petals absent; ovary of 3 (rarely 2) carpels, the ovules solitary in each locule, the styles elongated, free, bifid or bipartite. Fruits capsular, of 3 (rarely 1 or 2) cocci, the columella slender; seeds roundish, ecarunculate, smooth, endosperm present, the cotyledons broad, thin.
Trees or shrubs, monoecious or dioecious. Branchlets frequently glabrous. Leaves alternate, glandular-crenulate, penninerved; stipule small, deciduous. Inflorescences spicate or racemose, axillary; bracts eglandular. Male flowers fascicled to glomerulose, rarely solitary along axis; calyx closed in bud; sepals 3 or 4, valvate; petals absent; disk absent; stamens 25-80(-100); filaments free; anthers dorsifixed, 4-locellate, connective shortly produced; pistillode absent. Female inflorescences frequently 1-flowered. Female flowers: pedicel long, thickened at tip; sepals 3-5, imbricate, accrescent or scarcely enlarged in fruit; ovary 2-or 3-locular; styles 2 or 3, base often connate, deeply 2-cleft, filiform, stigmatic surface papillose; ovules 1 per locule. Fruit a capsule, 2-or 3-locular; pedicels rigid, club-shaped. Seeds subglobose, smooth, marbled.