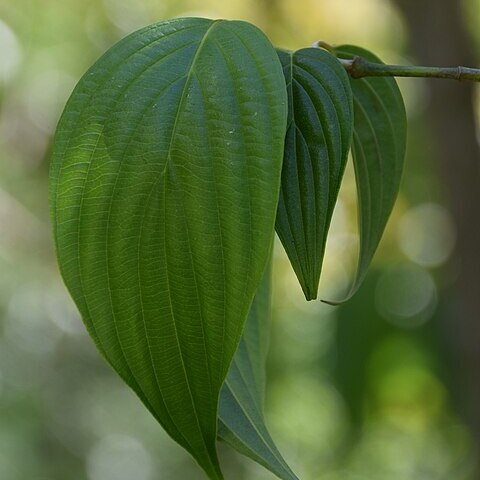
Trees 4–8 m tall; axis monopodial. Bark dark brown; winter buds of leaves terminal or axillary, narrowly conical. Flower buds in pairs, lateral, separated by terminal leaf bud, subglobose, pubescent with yellowish brown trichomes, apex acute. Leaf blade ovate-lanceolate to narrowly elliptic, 6–11 × 2.8–5.5 cm, abaxially sparsely pubescent with grayish white appressed trichomes and a cluster of conspicuous gray long trichomes in axils of veins, or sometimes tomentose, veins 5 or 6. Umbellate inflorescences lateral; bracts broadly ovate to elliptic, 6.5–7 mm, papery to leathery, both surfaces pubescent with appressed trichomes; peduncle purplish brown, 5–12 mm, ± pubescent. Pedicels 8–9 mm, slender, pubescent with long, yellow trichomes. Calyx triangular-lanceolate, ca. 0.7 mm. Petals lanceolate, ca. 4 mm. Stamens ca. 1.6 mm; anthers subglobose. Ovary campanulate, ca. 1 mm, pubescent with short gray trichomes; style 1–1.4 mm, glabrous. Fruit red or black (when ripe), oblong, 6–8(–10) × 3.4–4 mm; stones narrowly ellipsoid, ca. 7.5 mm, with few ribs. Fl. Apr, fr. Sep.
More
A deciduous tree. It is often 4-8 m tall but can grow 18 m tall. The leaves are narrowly oval and 6-11 cm long by 3-6 cm wide. The leaves are pale green. The veins are easy to see and the leaves are downy underneath. The flowers are yellow. The flowers appear before the leaves.
It is a warm temperate plant. It grows on slopes, margins of mixed forests, dense forests between 700-2500 (-3500) m in China. It suits hardiness zones 8-10. In Sichuan and Yunnan.
More
Dense forests, mixed forest margins, slopes; at elevations from 700-2 500 metres, occasionally to 3,500 metres.