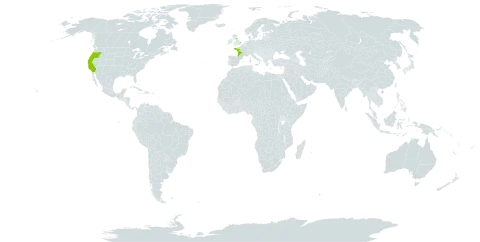
A cabbage family herb. It is a perennial plant up to 75 cm high. It spreads and forms mounds. The stems are thick. It has grey-green wavy edged leaves. The leaves can be up to 30 cm long. They are like cabbage leaves and arranged in a ring at the base. A robust flowering stalk comes from the centre of the leaves. The flowers are white and in clusters. These can be 0.6 m across.