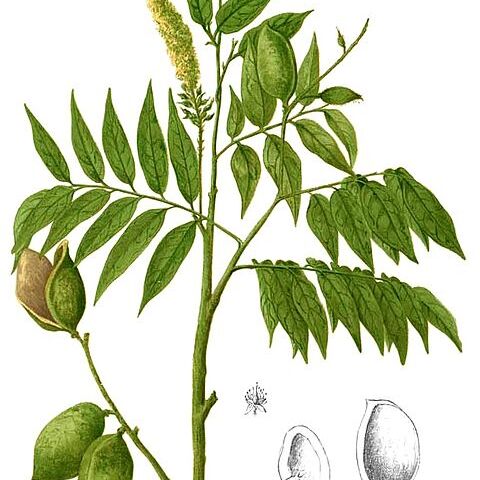
Trees or shrubs, rarely scramblers. Stipules usually intrapetiolar, small or rarely large, often connate (at the basal parts), sometimes interpetiolar and free, caducous or persistent. Leaves spiral, imparipinnate or seemingly paripinnate (sometimes with a prolonged tip of rachis beyond the apical leaflet, often deciducous), l-9(-13)-foliolate, petioled. Leaflets alternate, very rarely opposite; midrib usually slightly grooved above and elevated beneath; nerves slightly patent, ascending and arcuately anastomosing extending towards near the margin, usually slightly impressed above and prominent beneath; veins often faintly loosely reticulate, usually obscure or invisible above, obscure or sometimes distinct beneath; petiolules short. Inflorescences racemose, axillary or terminal, very rarely cauline (C. cauliflora), solitary or fasciculate; bracts entire or lobed (sometimes 3-lobed with the central lobe redivided), often caducous, sometimes persistent; bracteoles 2, (subopposite or alternate, often minute or small, or relatively large and enclosing the young flower buds, often caducous, sometimes persistent; pedicels rather short, articulated. Flowers bisexual. Hypanthium (or receptacle) shortly cupular or campanulate. Calyx lobes 4, imbricate, often ciliate on the margin, reflexed during flowering. Corolla absent. Disk absent (or a protruding rim or ring round the mouth of hypanthium). Stamens 10 or fewer, often caducous; filaments united at their basal parts, sometimes seemingly free, ± equal or slightly unequal in length; anthers small, ovoid, ellipsoid, or oblong, dorsifixed, longitudinally dehiscing. Pistil shortly stipitate, stipe free or (partly) adnate to the hypanthium; ovary elliptic or ovate, often densely hairy, 1-6-ovuled; style filiform; stigma terminal, small, knob-like. Pods obliquely orbicular, ellipsoid or ovoid, coriaceous or slightly woody, compressed or somewhat swollen, dehiscing, 2-valved, l_4(_6)-seeded. Seeds suborbicular or subreniform, compressed, cotyledons concave, exarillate, exalbuminous.
More
Unarmed trees. Leaves imparipinnate or seemingly paripinnate, the tip of the rachis often prolonged beyond the apical leaflet and caducous; stipules small or large, deciduous or subpersistent; leaflets 1-9, alternate or opposite. Flowers small, in axillary or terminal solitary or clustered racemes; bracts and bracteoles small, deciduous or subpersistent. Calyx tube short with the 4 imbricate lobes reflexed during flowering. Petals absent. Stamens 8-10, appearing free but joined into a basal tube which adheres inside the calyx tube; anthers versatile, small, longitudinally dehiscent. Ovary shortly stipitate, 1-6-ovulate; style filiform; stigma terminal. Pods round, elliptic, ovate or oblong, compressed or somewhat swollen, dehiscent; valves coriaceous or woody. Seeds usually 1 or 2, orbicular or subreniform, compressed.