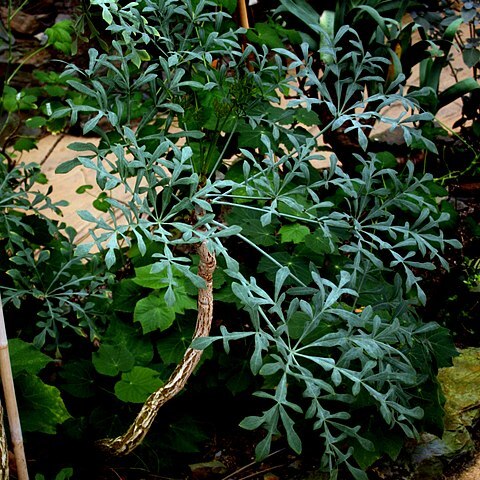
Evergreen trees up to 5 m high, monocaulescent, seldom polycaulescent and then with a maximum of 4 stems; trunk up to 300 mm in diameter, somewhat branched. Bark grey with longitudinal and transverse furrows, corky. Leaves alternate, petiolate and in rosettes on the ends of branches, always multidigitately compound and particularly complex. Petiole ridged, (140)170-435(480) mm long; leaf base prominent with two persistent stipules. Lamina leathery, grey-green with (5)7-9(11) primary leaflets (digits). Primary leaflets articulate and petiolate; ventro-lateral primary leaflets with at least one articulation; dorsal primary leaflets with (2)3-4 articulations; articulations without stipellae; midrib of primary leaflets not prominent abaxially; stalks of primary leaflets (30)40-70(90) mm long. Secondary leaflets lanceolate, margin entire, size and complexity of secondary leaflets decreasing basipetally on primary leaflets, in very complex leaves the secondary leaflets at articulation 2 larger than those at articulation 1; apical secondary leaflets (36)42-105(115) mm long and (11)14-26(30) mm wide in less compound leaves; if constricted and lateral tertiary leaflets occurring at the constriction (as in very complex leaves), the constriction then known as an articulation; lateral secondary leaflets of the first order at articulation 1 (for less compound leaves) or articulation 2 (for very compound leaves) (68)76-125(140) mm long and 9(11)-26(29) mm wide; lateral secondary leaflets of the second order usually present at articulations 1 and 2, (44)48-74(80) mm long and 8(10)-19(23) mm wide; sometimes lateral secondary leaflets of the first order at articulation 2 of verycomplex leaves having a secondary articulation on which tertiary lateral and tertiary apical leaflets are borne; lateral secondary leaflets of the second order usually absent at articulation 3; articulations 4 and 5 usually lacking lateral secondary leaflets. Flowering system of spikes borne in terminal compound umbels (bi-umbelled spikes); paracladia of first order 7-13, 100-140(160) mm long, intemodes elongated and leaf scars distinct; spikes borne in terminal umbel on paracladia of the first order; 7-11 spikes per paracladium; peduncle of spike 30-50(60) mm long and of rachis (90)115-150(180) mm long; dry spikes (15)20-30 mm in diameter. Flowers 7-9 mm long prior to anthesis, sessile, angular, densely packed on axis, each subtended by a single carinate hypsophyll with a denticulate margin. Sepals 5, fused and much reduced. Petals 5, valvate, 2-3 mm long, 2 mm broad at base, caducous. Stamens 5, alternating with petals, caducous; anthers oblong, two-locular, ovate, versatile, dorsifixed, introrse, 1.5-2 mm long; filament hookshaped, 1.5-2 mm long. Ovary inferior, bilocular; styles 2, not spreading, 0.5-1 mm long; stylopodium oblate, circular, with a peripheral ridge, rugous; ovule pendulous, one per locule. Fruit a conical purple drupe. Seed 5-7 mm long, 3-4 mm wide, plano-convex, anatropous, raphe ventral, testa brown.
More
Evergreen tree, up to 5 m high. Leaves multidigitately compound and glaucous; primary leaflets particularly compound; leaflets without prominent midrib; margins entire. Stipellae absent on articulations. Single hypsophyll subtending each flower. Flowers green.
A tree. It grows 5 m tall. The bark has deep cracks.
It is a subtropical plant. It grows on rocky slopes in hot, dry, wooded savannah. It can tolerate light frosts. It is best in a sunny position in a well-drained soil. Once established plants can tolerate drought.
More
Rocky slopes in hot, dry, wooded savannah.