Perennial from a short stout rhizome. Culms robust, up to 3 m tall, 1–2 cm in diam., nodes glabrous or pubescent. Leaf sheaths glabrous, auricles often present; leaf blades linear, up to 100 × 1.5 cm, scabrid, abaxial surface tomentose at sheath junction, adaxial surface pilose at base, otherwise glabrous, base gradually narrowed, apex filiform; ligule 2–5 mm. Spathate compound panicle very large, lax, decompound, grayish green, up to 60 cm or more, nodes bearded, branches numerous, drooping; spatheoles 1–2 cm; racemes 1–1.7 cm; rachis internodes and pedicels ciliate on margins; pedicel of homogamous pair not usually swollen. Sessile spikelet narrowly elliptic-oblong, 4–4.5 × 0.8–1 mm; lower glume flat or shallowly concave, usually slightly transversely wrinkled, sharply 2-keeled throughout, keels narrowly winged, wings 0.1 mm wide or less, obscurely 3-veined between keels; upper lemma awned; awn 0.8–1 cm. Pedicelled spikelet 3.5–4 mm. Fl. and fr. summer to autumn. 2n = 20, 40.
More
A grass. It keeps growing from year to year. It has a short stout rhizome. The culms are robust and 3 m tall. They are 1-2 cm across. The leaf blades are narrow and 100 cm long by 1.5 cm wide.
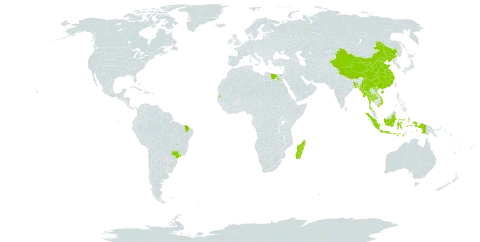
Grassy slopes below 1,000 metres in southern China. Fields, roadsides, in mixed deciduous, dipterocarp and teak forest, often on limestone, and on slopes and ridges at elevations of 100-2,200 metres.
More
It is a tropical plant. It is mostly grown in Kerala in India. In southern China it grows on grassy slopes below 1,000 m above sea level. In Yunnan.
The leaves and shoots are used in cooking. They are also used to extract oil. This is used in food manufacture for flavouring baked goods, fats and oils, ice cream, candy, drinks and chewing gum. Dried leaves are used in herbal teas.