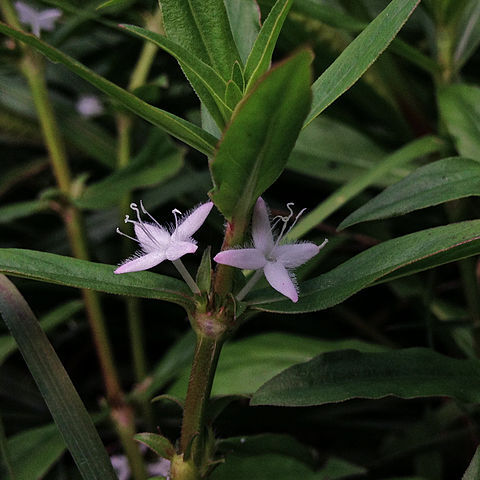
Annual or perennial erect or mostly decumbent or prostrate herbs; stems often 4-angled. Leaves opposite or sometimes appearing whorled due to the presence of reduced axillary shoots, ± sessile or shortly petiolate; blades linear to ovate; stipules with bases united to the petiole, divided into fimbriae. Flowers mostly small, not heterostylous, in small axillary clusters or, in one group of American species, terminal in spikes or capitula. Calyx-tube ellipsoid, ovoid or obconic; lobes 2–4 (rarely 5–6), sometimes with some small accessory teeth, ± persistent. Corolla-tube ± funnel-shaped, glabrous or hairy at the throat; lobes 4 (rarely 5–6), valvate. Stamens 4 (rarely 5–6), exserted, the filaments inserted at the throat. Ovary 2(rarely–3–4)-locular; ovules solitary in each cell, attached to the middle of the septum; style filiform exserted; stigma 2-lobed or ± capitate. Fruit of 2 (rarely 3–4) indehiscent cocci. Seeds oblong, dorsally convex, ventrally longitudinally grooved, rarely with a transverse groove or in one subgenus (Pleiaulax Verdc.) distinctly lobed.
Annual or perennial herbs, the stems terete or 4-angled. Leaves opposite or seemingly verticillate, sessile or short petiolate; stipules connate, united with the petioles, the sheath filiform setose, the processes often ciliate. Inflorescences axillary or in terminal spikes, the capitate heads borne in the axils of reduced leaves. Flowers sessile, usually 4-merous, the calycine tube 2-6-lobed, often with small interdental glands; corolla infundibuliform to hippocrateriform, the lobes 4-6; stamens 4-6, the anthers exserted, dorsifixed, the filaments attached at the mouth; ovary mostly 2-celled, the ovules solitary, adnate to the septum in the middle. Fruits partly superior, the 2 cocci indehiscent, the endocarp thick and woody, smooth or costate, the ventral face plane, the endosperm relatively re-mote from the hilar ridge.
Fls mostly 4-merous; sep 2–4, sometimes very unequal; cor salverform or funnelform, with slender tube and 4 short lobes; ovary bilocular, with a single axile ovule in each locule; fr dry, splitting into 2 nutlets; herbs, ours low and branched, with narrow lvs and small fls sessile in the axils. 50, mainly warm regions.
Leaves opposite or sometimes appearing whorled due to the presence of reduced axillary shoots, ± sessile or shortly petiolate; blades linear to ovate; stipules with bases united to the petiole, divided into fimbriae.
Calyx tube ellipsoid, ovoid or obconic; lobes 2–4(rarely 5–6), sometimes with some small accessory teeth, ± persistent Corolla tube ± funnel-shaped, glabrous or hairy at the throat; lobes 4 (rarely 5–6), valvate.
Ovary 2 (rarely 3–4)-locular; ovules solitary in each cell, attached to the middle of the septum; style filiform, exserted; stigma 2-lobed or ± capitate.
Seeds oblong, dorsaTly convex, vena-ally longitudinally grooved, rarely with a transverse groove or in one subgenus (Pleiaulax Verdc.) distinctly lobed.
Flowers mostly small, not heterostylous, in small axillary clusters or, in one group of American species, terminal in spikes or capitula.
Annual or perennial erect or mostly decumbent or prostrate herbs; stems often 4-angled.
Stamens 4 (rarely 5–6), exserted, the filaments inserted at the throat.
Fruit of 2 (rarely 3–4) indehiscent cocci.