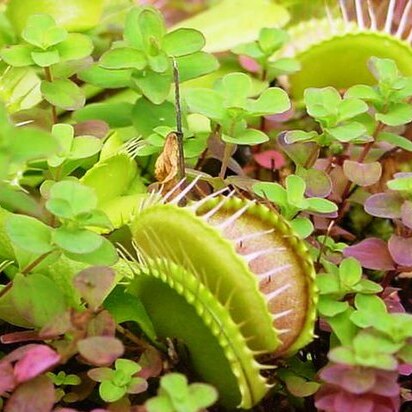
Herbs, annual or perennial, carnivorous, scapose. Leaves in basal rosettes (alternate-cauline in Drosera intermedia); stipulate or estipulate; petiolate; blade infolded or circinate in vernation, modified as hinged, jawlike trap (Dionaea) [Aldrovanda] or bearing mucilage-tipped, irritable, multicelled hairs (Drosera) [Drosophyllum]. Inflorescences terminal, umbel-like cymes (Dionaea) or lateral, circinate or scorpioid cymes (Drosera), multiflowered (rarely 1-flowered). Flowers: perianth and androecium hypogynous; sepals 5, distinct or connate basally; petals 5, distinct; stamens usually 5 (Drosera) or (10–)15(–20) (Dionaea), distinct or sometimes connate basally; pistils 1, compound, 3–5-carpellate; ovary superior, 1-locular; placentation basal (Dionaea) or parietal (Drosera); styles 1 and undivided (Dionaea) or 3[5] and bifid (Drosera); stigma plumose (Dionaea) or capitate (Drosera). Fruits capsular.
Herbs with tubers or small rhizomes, sometimes ephemeral. Leaves rosetted, whorled or alternate; lamina with insect-trapping glandular hairs, or sensitive bristles which trigger closing of lamina to trap insects; stipules present or absent. Flowers actinomorphic, bisexual, in cymes, racemes or solitary, axillary, lateral or terminal. Sepals 4 or 5, free or shortly united. Petals 4 or 5, sometimes more, free. Stamens 4 or 5, hypogynous, free, alternate with petals; anthers bilocular, opening by longitudi– nal slits. Ovary superior, unilocular, 3–5–carpellate; placentation parietal; ovules many; styles 2–5, simple or branched. Fruit a loculicidal capsule within persistent calyx. Seeds small, with endosperm.
Insectivorous herbs. Leaves in whorls or spirally arranged. Flowers in racemes or cymes or occasionally solitary, regular, hypogynous, hermaphrodite. Sepals 4–8, imbricate, basally connate. Petals 4–8, imbricate, free, convolute. Stamens 5–20 in 1 or more whorls. Ovary superior, syncarpous, 3–5-carpellary, unilocular; styles 3–5, free or somewhat united, simple or branched; ovules numerous, on 3–5 parietal placentas or a free-basal placenta. Fruit a loculicidal capsule. Seeds small, with endosperm
Ovary superior, syncarpous, 3–5-carpellary, 1-locular; styles 3–5, free or more or less united, simple or branched; ovules numerous, on 3–5 parietal placentas or a free basal placenta
Stamens 4–20, often 5, hypogynous, free or rarely united at the base; anthers 2-celled, extrorse, opening by longitudinal slits
Herbs, often stemless with rosettes of leaves, the latter usually covered with sticky stipitate glands which entrap insects
Stamens 5–20 in 1 or more whorls; filaments free or united at the base; anthers 2-locular, dehiscing by longitudinal slits
Leaves in whorls or alternate, frequently in basal rosettes; lamina with glandular excrescences; stipules usually present
Ovary free, 1-celled, with parietal or subbasal placentas; ovules many or rarely few; styles 3–5, mostly free
Flowers in racemes or cymes or occasionally solitary, actinomorphic, hypogynous, bisexual
Seeds numerous, with fleshy endosperm; embryo straight; cotyledons short
Flowers actinomorphic, hermaphrodite, in usually simple circinate cymes
Sepals 5–4, more or less connate at the base, imbricate, persistent
Petals 5, hypogynous, very rarely perigynous, nervose
Annual or perennial insectivorous herbs
Sepals 4–8, basally connate, imbricate
Seeds small, with endosperm
Fruit a loculicidal capsule
Fruit a loculicidal capsule
Petals 4–8, free, imbricate