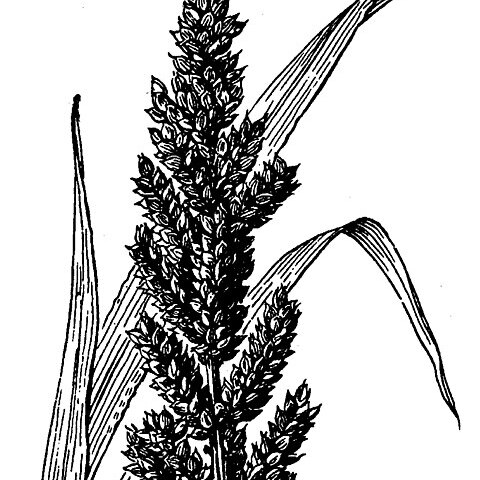
A cereal or millet. It is an annual grass. The culms are robust. It grows 1-1.5 m tall. The leaf sheaths are smooth. The leaves are broad. The leaf blade is soft and narrow. It is 15-40 cm long and 1-2.4 cm wide. The edges are thickened and wavy. The flower is erect and sword shaped. It is 10-20 cm long. The racemes are 1-3 cm long and closely spaced and overlapping. The spikelets are greenish. The grains are oval and light brown to purple.