Herbs annual, aquatic. Stem prostrate, slender, rooting at nodes. Leaves opposite or verticillate, shortly petiolate; leaf blade small, margin usually entire. Flowers usually only 1 per node, very small. Sepals 2-4, united at base, membranous, apex subacute. Petals 2-4, longer than sepals, apex obtuse. Stamens 1 or 2 × as many as petals. Ovary globose, compressed, 2-4-loculed, apex truncate; ovules numerous; styles 2-4; stigmas capitate. Capsule membranous, 2-4-septicidal. Seeds straight, curved, or horseshoe-shaped, surface reticulate-striate with hexagonal or elliptic pits.
Annual herbs, prostrate to erect, often aquatic. Leaves opposite or whorled, entire; stipules persistent or not. Flowers solitary in the axil of only one leaf in any pair, minute, 3-merous. Sepals membranous. Petals as many as sepals, falling. Stamens as many as or twice the number of petals, shorter to longer than the sepals. Styles 3, short, capitate. Ovary 3-locular. Capsule with membranous or thickish walls, with a terminal depression. Seeds straight or curved, surface reticulated.
Small glabrous herbs of swampy, muddy or inundated localities. Leaves in the Malaysian species opposite, shortly stalked. Flowers solitary, minute, 2-4-merous. Sepals shortly connate at the base, obtuse, nerveless. Petals exceeding the sepals, broadly oval, white or pink. Stamens as many as petals or twice their number. Ovary globose. Fruit globose with an impressed apex and a very thin transparent wall. Seeds numerous, straight or curved, with a scalariform reticulation.
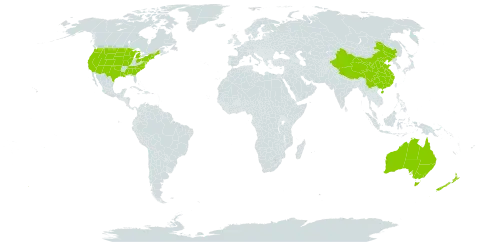
Sep and pet each 2–4; stamens as many (in our spp.) or twice as many as the sep; ovary 2–4-locular, the placentas axile or basal-axile; seeds several per cell, cylindric, minutely areolate; small aquatic annuals with inconspicuous axillary fls and thin-walled frs. 20, widespread.
Sepals and petals 2-4; stamens and styles same number or twice as many as petals. Capsule membr., 2-4-celled and valved; seeds us. ∞.About 15 temperate and tropical spp.
Fruit globose; somewhat depressed at the apex, wall membranous; seeds numerous, straight or curved; testa with a scalariform reticulation.
Leaves opposite or more rarely verticillate; stipules present.
Ovary globose, 3–4-locular; styles minute, 3–4, spreading.
Small glabrous herbs, aquatic or found in damp situations.
Stamens as many as the petals or twice the number.
Sepals 2–4 shortly connate at the base, obtuse.
Flowers minute, solitary in the leaf axils.
Petals 2–4, free, white or pink.