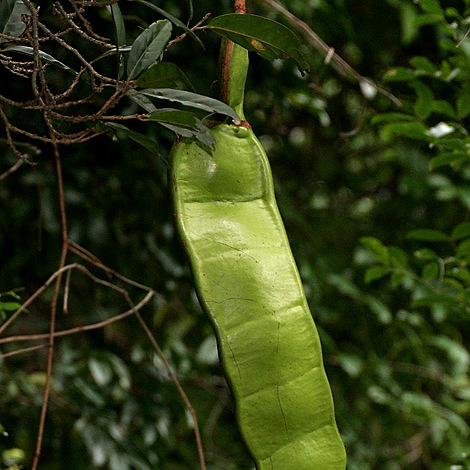
A creeping shrub. It has a long stem that is climbing. It can be 50 m long. The stems can be large and can be 30 cm across. The stems are angled and twisted. The leaves have 1 or 2 pairs of leaflets stalks. There are 3-5 pairs of leaflets on each stalk. These are oblong and 9 cm long by 4 cm wide. There is a forked tendril at the end. The flowers are in long spikes in the axils of leaves. These are up to 23 cm long. These hang in the axils of side branches. The flowers are pale yellow. The fruit are large woody pods 2 m long by 15 cm wide. It is jointed. There are 10 seeds. They are oval and flattened. They are flat and woody but break into single seeded pieces. The seeds are 4.5 cm long by 5 cm wide and very hard.
Climbers, woody. Pinnae 2 pairs, 5-15 cm; leaflets 3 or 4(or 5) pairs per pinna, opposite, obovate to elliptic-lanceolate, unequally sided, 2.3-7 × 1.3-3.5 cm, papery, abaxially glaucous, base rounded to broadly cuneate, apex acuminate to obtuse, or emarginate. Spikes solitary or fasciculate, axillary, 12-25 cm. Flowers male or bisexual. Calyx green, cup-shaped, 0.8-1 mm. Petals white, narrowly elliptic to lanceolate, 2.8-3 mm. Stamens white, turning yellow, 5-6.5 mm. Ovary glabrous. Legume straight to slightly curved, to 2 m × 7-15 cm; segments 6.5-7.5 cm, epicarp and endocarp woody. Seeds brown, brilliant, suborbicular, flat, 3.5-4 × ca. 1 cm. Fl. Mar-Apr, fr. Aug-Oct.