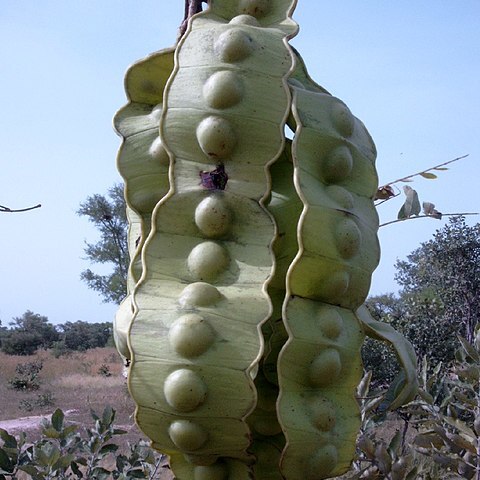
Woody vines or climbing shrubs or trees, usually very large, unarmed (in Panama) or aculeate, sometimes cirrhiferous. Leaves large, bipinnate, the pinnae few pairs (in Panama) or less frequently several to many, opposite, the leaflets few to many pairs; petiole and usually the rachis eglandular, the rachis sometimes terminating in a bifurcate tendril; leaflets large or small; stipules small. Inflores-cence of usually elongate spikes, these solitary and borne from foliate branches or clustered terminally in a large raceme; floral bracts minute. Flowers small, usually briefly stipitate, 5-parted, valvate, variously colored, often with a disagreeable odor; calyx small, synsepalous, broadly and shallowly cupulate; corolla of 5 free or slightly coherent petals; stamens 10, free, briefly exserted; anthers tipped with a (caducous) gland; ovary several-to many-ovulate; style slender; stigma terminal, truncate. Legume often very large (Panamanian species), flat, straight or curved, the valves in time breaking into segments, the margins continuous and persistent.
Unarmed lianas or scandent shrubs (in Asia). Stipules not spinescent, inconspicuous. Leaves bipinnate, not sensitive to the touch, rachis and pinnae without extrafloral nectaries, the terminal pinnae transformed into tendrils; leaflets opposite or proximal leaflets (in one species) alternate. Inflorescence a pedunculate, axillary or supra-axillary spike or spiciform raceme. Flowers pentamerous, uniform, male or bisexual. Calyx connate, valvate. Petals valvate, free, or shortly united at the base. Stamens 10, free; anthers with a subsessile or stipitate caducous gland at the top of the connective. Pods often large, char-teceous or mostly woody, straight, curved or spirally twisted, at maturity falling apart in o le-seeded segments; the exocarp separating from the endocarp, which forms envelopes containing one seed, the sutures remaining as an empty frame. Seeds globular, flattened or irregularly compressed, with a hard testa without areole (in Asian species), wingless, aril absent, endosperm absent; cotyledons large, radicle curved.
Climbers, woody, or scandent shrubs, large, usually unarmed. Leaves bipinnate; stipules small, setaceous; petiolar gland absent; terminal pair of pinnae sometimes transformed into a tendril; leaflets opposite, 1 to many pairs. Spikes axillary or supra-axillary, slender, solitary or arranged in a racemelike panicle. Flowers bisexual or polygamous, 5-merous, sessile. Calyx campanulate, shortly dentate. Petals free or slightly united at base. Stamens 10, shortly connate at base and adnate to petals, much exserted; anthers with a deciduous gland at apex; filaments filiform. Ovary subsessile; ovules numerous; style filiform; stigma minute. Legume straight or curved to spirally twisted, plano-compressed, large and long, leathery or woody; valves splitting transversely at maturity into 1-seeded segments; segments falling away from suture, which persists as an empty frame. Seeds globose to orbicular, large; testa brown, thick, without pleurogram (in Asia).
Unarmed lianes. Leaves bipinnate; leaf axes lacking extrafloral nectaries; pinnae 1-2-jugate, terminal pair modified to tendrils; leaflets 1-4 (-5)-jugate, opposite. Inflorescence axillary or supra-axillary spikes, elongate, pedunculate. Flowers sessile (in Australia), 5-merous; sepals valvate, connate; petals valvate, free or united basally. Stamens 10, free; anthers with terminal gland. Pod woody and straight or curved (in Australia), breaking apart from sutures into 1-seeded segments. Seeds flat to compressed; pleurogram absent.
Pods straight or curved, flat or rarely spirally twisted, sometimes very large; at maturity the valves (but not the margins) splitting transversely into 1-seeded segments from which the outer layer (exocarp) of the pod-wall often peels off, the inner layer (endocarp) persisting as a closed envelope round the seed; the segments falling away from the margins, which persist as a continuous but empty frame.
Petals 5, free or nearly so (or ± connate in species not occurring in our area), separated from the ovary-base by a very short perigynous zone composed of stamens adnate to an apparent corolla-tube.
Inflorescences of spiciform racemes or spikes, which are axillary or supra-axillary, solitary or clustered and often ± aggregated.
Seeds (in the African species at least) ± compressed, mostly elliptic or subcircular in outline, deep brown, smooth.
Trees, shrubs, suffrutices or lianes; prickles absent or sometimes present.
Stamens 10, fertile; anthers with a usually very caducous apical gland.
Leaves 2-pinnate; pinnae each with one to many pairs of leaflets.
Calyx gamosepalous, with 5 teeth.
Flowers hermaphrodite or male.