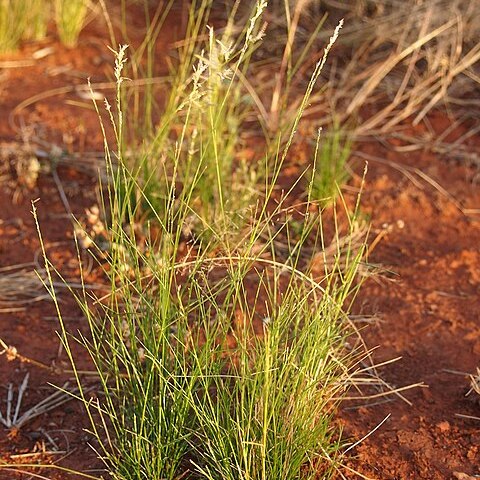
Compactly tufted or tussock-forming perennials, eglandular; rootbase thickened or knotted, hairy; cataphylls coriaceous, glossy. Culms erect, 12–60 cm high, wiry. Leaves mostly glabrous, usually scaberulous; sheath abruptly wider than blade; ligule c. 0.5 mm long; blade rolled or rarely flat, straight, filiform, firm-pointed. Panicles contracted, 6–9 cm long, 2–4 cm wide; branches entirely spikelet-bearing or naked near axil. Spikelets distinctly but shortly pedicellate, linear, 4–15 (–32) mm long, 1.3–2.3 mm wide, straight or curved; rachilla straight; florets 9–30 (–70), closely overlapping and becoming loose. Glumes ±equal, ovate, 1–1.3 mm long. Lemma ovate, c. 1.5 mm long, obtuse, membranous with hyaline margins, 3-nerved, scaberulous or smooth. Palea as long as lemma (sometimes longer); body obovate or spathulate; keels short and dividing palea into 3 lobes; flaps distinctly narrower than body. Stamens (2–) 3; anthers 0.5–0.8 mm long. Grain strongly dorsally compressed, oblong-ellipsoid, c. 0.5 mm long, usually concave on back.
More
A grass which keeps growing from year to year. It grows 20-45 cm high. It forms clumps which spread slowly. The leaves are 4-13 cm long by 0.1-0.3 cm wide. The are narrow and can be flat or rolled inwards. They are rough on the upper surface. The edges are thickened and sharp. The stems are 20-45 cm long and slender and wiry. The branched flower head is 7-10 cm long by 1-2.5 cm wide. There are separate clusters of spikelets. These are green and 1-1.5 cm long. They are flattened.
Commonly in red, brown, grey or blackclay and clayey loam plains and stony tablelands; often in alluvial, seasonallyflooded habitats, sometimes in saline or calcareous and sandy soils and disturbedsites.
More
It grows in inland areas in Australia. It grows in tropical and subtropical places. It grows in loose clusters on the beds of occasional streams. It is very hardy. It can grow in arid places.