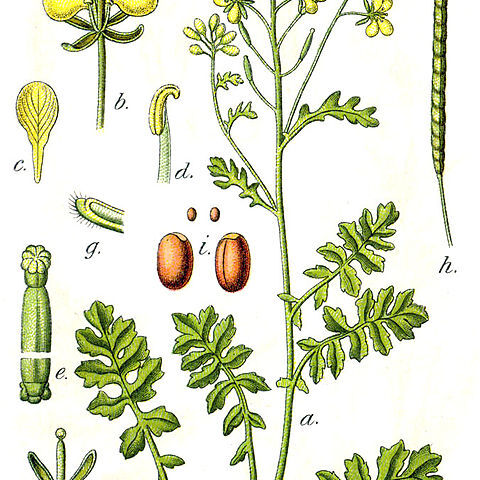
Annual, biennial or perennial herbs (rarely subshrubs) with a taproot, little to moderately branched, usually with simple hairs. Basal leaves ± lyrate-pinnate. Racemes terminal, bracteate or ebracteate, ± corymbose, with small flowers, in fruit elongate, lax. Sepals not spreading, the inner slightly saccate. Petals yellowish or white, spathulate. Stamens 6, distinctly tetradynamous, with linear filaments. Nectaries 2-lobed or horseshoe-shaped (with opening outwards) at the base of the lateral stamens, and as a spheroid gland outside each median stamen-pair. Gynophore absent or very short; ovary cylindrical, with short style and semiglobose to bifid stigma; ovules 10–50. Fruit a siliqua, readily dehiscent, linear, usually 4-angled in transverse section, with a seedless conical beak; valves with a prominent midnerve. Seeds usually uniseriate, spheroid to ellipsoid, slightly flattened, finely reticulate, not mucilaginous.
Sep erect to spreading, somewhat cucullate at the tip; pet yellow, spatulate; each pair of long stamens subtended by a short, pyramidal gland; a short gland between the ovary and each short stamen; ovary cylindric; ovules numerous; style very short; stigma capitate; fr elongate, 4-angled, conspicuously beaked, the valves sharply 1-nerved; seeds ovoid or oblong, in 1 row in each locule; herbs with pinnatifid lvs, the pubescence of simple hairs or none. 17, mainly Mediterranean.
Silique quadrangular with keeled valves, each with 1 prominent dorsal nerve and a conical beak with 0–3 seeds.
Annual, biennial or perennial herbs usually ± hairy with simple hairs.
Lower leaves lyrate-pinnatifid, upper ones usually linear.
Sepals erect or spreading, inner pair somewhat saccate.
Flowers yellow in bracteate or ebracteate racemes.
Cotyledons longitudinally conduplicate.
Seeds 1-seriate, ovoid or ellipsoid.
Petals 4, unguiculate.
Stamens 6.