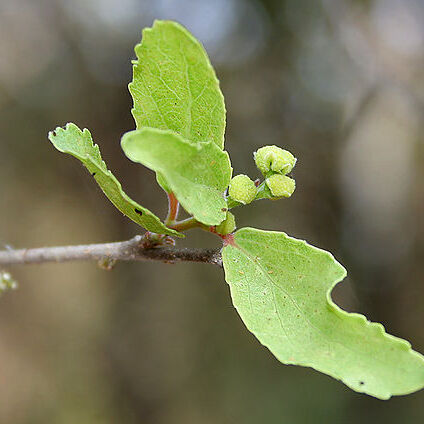
Trees or shrubs, usually not heterophyllous, not clonal; branching sympodial. Stems usually spinose, sometimes unarmed, spines simple and/or compound. Leaves usually persistent, sometimes deciduous; stipules minute; petiole not glandular. Inflorescences axillary or terminal (on lateral twigs), few-flowered, racemelike cymes [2-flowered fascicles], pistillate flowers sometimes solitary. Pedicels articulate near base. Flowers (unisexual and/or bisexual, fragrant [not]); sepals 4-7; disc lobed; stamens ca. 15-30; filaments distinct; ovary [2-]5-7[-10]-carpellate (and-locular, placentation axile, placentae intruded and fused); styles (persistent) connate basally [entirely and columnar]; stigma notched-capitate or truncate. Fruits drupaceous. Seeds: aril absent. x = 11.
Dioecious trees or shrubs, often spinose. Leaves spirally arranged, serrate or crenate; stipules minute or absent. Flowers in short axillary or terminal racemes, or solitary. Sepals 4–7, imbricate. Petals absent. Disc entire, crenulate or of free glands, extra-staminal. Male flowers with 15 to many free stamens; anthers extrorse, dorsifixed, versatile; no rudimentary ovary. Female flowers: ovary superior, made incompletely 2–10–1ocular by false septa of protruding placentas; ovules 2 per locule; styles as many as locules, free or connate; stigmas notched or bilobed. Fruit a fleshy drupe, the locules developing into 1-or 2-seeded pyrenes. Seeds obovoid; testa thinly crustaceous.
Female flowers with a usually entire or crenulate disk, ovary incompletely (2) 4–6 (10)-locular by false septa; ovules 2 per loculus one above the other; styles as many as the loculi, free or connate, persistent.
Male flowers with an extrastaminal disk usually broken into free glands; stamens 15–?, anthers dorsifixed, rudiment of ovary 0.
Flowers dioecious, rarely bisexual, small, in short axillary racemes or solitary.
Fruit a fleshy berry with 4–16 seeds usually in pairs one above the other.
Shrubs or trees; branches often spinose, trunk occasionally spinose.
Sepals 4–7, slightly connate at the base, imbricate.
Seeds obovoid; cotyledons ± orbicular.
Leaves petiolate, mostly crenate.
Petals 0.