Shrub or tree, generally spiny, up to 10 m. tall; bark rough; spines of the trunk sometimes branched, up to 12 cm. long.. Vegetative parts varying from glabrous to densely pubescent.. Leaves also variable in shape and size; blade ovate or elliptic, sometimes suborbicular or obovate, apex obtusely acuminate, obtuse or rounded, base cuneate to rounded, membranous to almost coriaceous, serrulate-crenate, or more rarely subentire, 2.5–12(–16) cm. long, 2–8 cm. broad; lateral nerves 4–7 pairs, slightly prominent on both faces, as is the ± dense reticulation; petiole up to 2 cm. long.. Flowers dioecious, or occasionally bisexual (1 or several branches of a ♀ specimen with perfect flowers, which, however, bear fewer stamens than in the ♂ ones).. Male flowers in axillary racemes 0.5–2 cm. long; pedicels slender, ± pubescent, up to 1 cm. long, the basal bracts minute and caducous.. Sepals broadly ovate, apex acute to rounded, pubescent on both sides, 1.5–2–5 mm. long and broad.. Filaments 2–2.5 mm. long; anthers 0.5 mm. long.. Disk lobulate.. Female flowers in short racemes or solitary; pedicels up to 5 mm.. Disk lobulate, clasping the base of the ovoid ovary.. Styles 4–8, central, connate at the base, spreading, up to 1.5 mm. long; stigmas truncate.. Fruit globular, reddish to reddish black when ripe, fleshy, up to 2.5 cm. across, with persistent styles, up to 10-seeded.. Seeds 8–10 mm. long, 4–7 mm. broad; testa rugose, pale brown.. Fig. 20.
Shrubs or small trees, 2-4 m tall, deciduous; bark gray-yellow, fissured, flaky; old branches usually not spiny; young branches with axillary, simple spines; branchlets puberulous or subglabrous. Petiole red, short, 3-5 mm, puberulous; leaf blade greenish abaxially, deep green adaxially, rose red when young, obovate to oblong-obovate, 2-4 × 1.5-3 cm, thickly papery, abaxially glabrous or sparsely pubescent, hairs spreading and short, adaxially glabrous, midvein raised abaxially, flat adaxially, lateral veins 5-7 pairs, reticulate veins conspicuous, base mostly acute to obtuse, margin serrulate above middle, apex rounded, sometimes retuse. Inflorescences axillary or terminating short lateral twigs, racemose, short; rachis 0.5-2 cm, puberulous. Pedicels 3-5 mm, puberulous, hairs spreading. Sepals 5 or 6, ovate, ca. 1.5 mm, outside glabrous or with a few scattered short hairs, inside sparsely to densely pubescent, margin white ciliate in dried material, apex obtuse. Staminate flowers: stamen filaments 2-2.5 mm, pubescent or less often glabrous. Pistillate flowers: ovary globose, placentas 5 or 6; styles 5 or 6, united only at base, radiating, 1-2 mm, slender. Fruit dull to blackish red, globose, 8-10 mm in diam., longitudinally 5-or 6-angled, styles persistent. Seeds 5 or 6. Fl. Jan-Mar, fr. Mar-Jul.
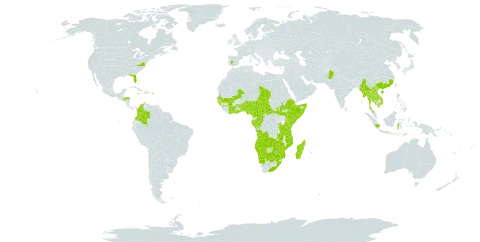
Tree or shrub, 1.5-16 m high. Bark smooth, stippled white (teste De Winter 7748) or rough and yellowish or orange-brown, occasionally silvery on young branches (Wild I.e.). Branches with or without axillary straight spines, sometimes with branching spines up to 12 cm long on the trunk near the base or with very spiny coppice shoots, glabrous or pubescent. Leaf-blade elliptic, ovate or obovate, 5-9.5 cm long, 3.5-6 cm wide, apex acuminate, acute or rounded, base cuneate to rounded, margins crenate, crenate-serrate or entire, veins 4-6 pairs, more prominent on lower surface, chartaceous, glabrous to densely pubescent; petiole 4-10 mm long, channelled above, glabrous or pubescent. Flowers dioecious or bisexual, greenish. Calyx segments or sepals often unequal, narrowly to broadly ovate, 2-3 mm long, 1.5-3 mm wide, ciliate. Male flowers: Stamens very numerous, surrounded by disc of fleshy free glands; filaments terete, 2.2 mm long. Female flowers: ovary globose c. 3 mm diam., surrounded by an annular disc; styles 4-8, channelled above; stigmas retuse. Bisexual flowers as female flowers, but with up to 10 stamens. Fruit red, globose, up to 3 cm diam., fleshy with persistent styles. Seeds c. 10, obovoid, subcompressed, c. 7 mm diam.; testa beige, hard, rough.
Trees or shrubs, 3-5(-10) m. Leaves: petiole 1-2 cm; blade red to pink when immature, ovate to orbiculate, 8-12 cm, becoming coriaceous, margins glandular-serrate or-crenate, surfaces glabrous or sparsely to densely pubescent. Peduncles 5-10 mm. Pedicels 5-10 mm. Flowers: bisexual ones sometimes on some branches of otherwise pistillate plants; sepals (persistent) slightly connate, greenish, ovate-orbiculate, 1.5-2.5 mm, apex acute to rounded, surfaces pubescent; filaments pubescent at base; ovary ovoid; styles spreading. Drupes reddish to purple or red-black at maturity, globose or ellipsoid, 1.8-2.5 cm. Seeds ca. 4-10, obovoid, 8-10 mm; testa crustaceous, rugose. 2n = 22 (India, cult. Cuba), 44 (Africa).
A shrub or small tree. It grows 5-15 m high. The trunk is crooked and low branched and armed with scattered slender spines. The leaves are alternate, pointed at the base and rounded at the tip. The edges of the leaves toothed with rounded lobes. Leaves are dark green on top and pale green underneath. They are 6-17 cm long and 3-7 cm wide. Male and female trees occur. The flowers are small and white, occur singly or in pairs in the axils of leaves or near the ends of short branches. The fruit are rounded, fleshy, purple or nearly black. They are smooth and about 1 cm across. The flesh is yellowish, juicy and acid. There are 6 to 10 small flattened seeds inside. The fruit are edible.
Leaf-lamina 2.5–12 x 1.3–7.5 cm., very variable, membranous or coriaceous, suborbicular, ovate, elliptic, obovate or ovate-elliptic, apex rounded, obtusely or rarely obtusely acuminate at the apex, base usually cuneate, occasionally rounded, margins crenate, crenate-serrulate or subentire, nerves in 4–7 pairs, slightly prominent above and below, venation laxly reticulate; petiole up to 1.3 cm. long.
Shrub or small tree up to 10 m. tall, with the bark rough and yellowish or orange-brown, occasionally silvery on young branches; axillary straight spines present or absent on the branches, sometimes with fearsome branching spines up to 12 cm. long on the trunk near the base or with very spiny coppice shoots.
Flowers dioecious or occasionally bisexual in short axillary racemes or occasionally solitary in the axils; peduncles very short; rhachis up to 2 cm. long, ± pubescent; pedicels up to 1 cm. long, ± pubescent, with caducous, deltoid, pubescent bracts at the base.
Female flowers with a lobulate, fleshy, glabrous disk clasping the base of the ovary; ovary ovoid, glabrous; styles 4–8, 0.5–1.5 mm. long, spreading, longitudinally grooved above; stigmas truncate.
Fruit reddish or reddish-black when ripe, up to 2.5 cm. in diam., fleshy, globose, becoming sulcate when dry, glabrous, with persistent styles, up to 10-seeded or thereabouts.
Male flower with very numerous stamens on filaments c. 2.5 mm. long, often with lobulate, glabrous glands forming a disk around the outer stamens.
Sepals 1.5–2.5 x 1.5–2.5 mm., imbricate, united for about 1 mm. at the base, broadly ovate, acute or rounded at the apex, pubescent on both sides.
All the vegetative parts except the older branches vary from quite glabrous to densely pubescent.
Seeds c. 8 x 7 mm., obovoid and somewhat flattened; testa pale brown, rugose.
Bisexual flowers similar to the female but with c. S stamens.