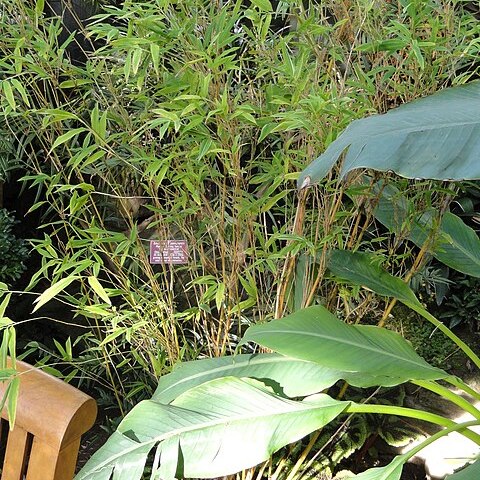
Clump-forming, fountain-like; rhizomes not running. Culms initially erect and wand-like, later arching over, 2-2.5 m, glaucous-white when young, becoming medium to deep green. Culm-sheath uniformly green or purplish green; ligule 1-5 mm, puberulent; auricles and bristles 0; sheath-blades linear-subulate. Branches many at each node, small, densely tufted. Leaf-sheath green or purplish, glabrous excepting margins sometimes ciliate. Ligule prominent, oblong, minutely puberulent. Leaf-blade usually 4-12-(15) × 0.4-0.8-(1.3) cm, narrow lanceolate or linear-lanceolate, long acuminate. Panicles large and diffuse. Spikelets 8-12 mm, often purple or strongly flushed purple. Glumes < florets, unequal, minutely puberulent; lower ¾-⅚ length of upper. Lodicules c. 2 × 2 mm, ciliate. Caryopsis 6-7 mm, blackish.
A bamboo. It grows 4 m tall. It is often striped with yellow and purple. The sheath of the stem is bullet shaped. The culm is 2 cm across.