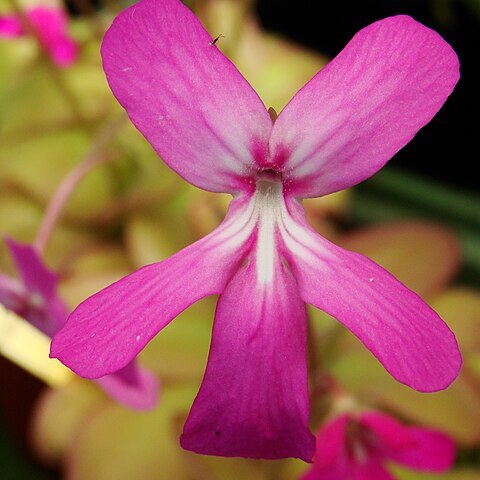
Herbs, perennial or annual, carnivorous, terrestrial, epiphytic, or aquatic. Roots present or absent. Stems often (Utricularia) modified into rhizoids, stolons, or rhizomes, rarely developed. Traps (bladders) on rhizoids, stolons, or leaves present in Utricularia but absent in Pinguicula. Stipules absent. Leaves alternate or in a basal rosette, simple or variously divided. Inflorescences usually racemes or reduced to a solitary flower; peduncle erect to twining. Flowers ± zygomorphic. Calyx 2-5-lobed or-parted; lobes imbricate, persistent. Corolla gamopetalous, tube short, limb 2-lipped or equally 5-lobed; lower lip entire or 2-or 3(-6)-lobed, lobes imbricate; upper lip entire or 2-or 3-lobed; spur subulate, cylindric, conic, or saccate. Stamens 2, inserted at base of corolla tube, included; filaments linear, short, curved or straight; anthers dorsifixed, ellipsoid; thecae 2, divaricate, confluent or (in Utricularia) sometimes distinct and ± separated by a connective; staminodes absent. Disk absent. Carpels 2, connate; ovary superior, 1-locular; placenta free-central or basal; ovules 2 to numerous, anatropous, somewhat sunken into placenta; style 1 or absent; stigma 2-lipped, upper lip reduced or obsolete. Fruit usually a capsule, loculicidal, circumscissile, or rarely indehiscent. Seeds few, numerous, or rarely 1 per capsule, minute, without endosperm.
Annual or perennial terrestrial, epiphytic (not in Australia) or aquatic carnivorous herbs with stems or leaves modified to capture prey, hairs glandular. Usually lacking true roots with stems modified to function as roots, sometimes with tubers (Utricularia). Leaves in a basal rosette or alternate, opposite or in whorls along stolons, sometimes apparently absent, simple and entire or pseudodichotomous (Utricularia) or pinnate (Utricularia), petiolate or sessile, sometimes with winter leaves differing from summer leaves (not in Australia). Inflorescence terminal or lateral, racemose, often reduced to a single flower, bracteate, prophylls present or absent. Flowers bisexual, zygomorphic. Calyx 2-or 4-(Utricularia) or 5 (not in Australia)-lobed, sometimes divided almost to base (Genlisea), usually 2-lipped. Petals 5, fused, 2-lipped, often forming a spur; upper lip usually entire or 2-lobed; lower lip entire or 2–5-lobed, often with a gibbous palate. Stamens 2, inserted at base of upper corolla lip; anthers 2-locular, dehiscing by longitudinal slits. Ovary superior, 2-carpellate, 1-locular; ovules few to several, rarely 2 (not in Australia); placentation basal or free-central; stigma often sessile, 2-lobed. Fruit a capsule, dehiscing by a slits, circumsessile or apparently indehiscent; seeds numerous, rarely 1 (not in Australia), without endosperm.
Ovary superior, unilocular; carpels 2, median; style simple, usually short or very short, rarely longer and geniculate; stigma more or less bilabiate, the superior lip usually smaller than the inferior or more or less obsolete; placenta free, basal, usually ovoid or globose; ovules usually numerous, sessile, rarely fewer or 2, anatropous
Corolla gamopetalous, bilabiate usually spurred, rarely saccate, usually violet or yellow; tube very short; superior lip interior, more or less entire or 2 or rarely more lobed; inferior lip entire or 2–5-lobed, usually with a raised more or less gibbous palate
Inflorescence terminal or lateral, peduncled, racemose, bracteate, or solitary, scapose; lowest bracts (scales) usually barren; bracteoles 2 or absent or more or less connate with the bract, usually at the base of the pedicels
Stamens 2, anticous, inserted at the base of the corolla; filaments usually short, usually curved, rarely longer and geniculate; anthers 2-thecous; thecae diverging, usually more or less confluent, dehiscing by a common slit
Calyx deeply 2–4 or 5-partite, almost regular or more or less bilobed or the sepals free to the base, persistent and often accrescent
Inflorescence racemose, bracteate, those of some aquatic species supported on the water by a whorl of modified spongy leaves (floats)
Stamens 2, attached at the base of the corolla, filaments often winged; anthers 2-celled, dorsifixed, the cells sometimes confluent
Fruit a unilocular capsule, 1-many-seeded, dehiscing by longitudinal slits or by pores or circumscissile or rarely indehiscent
Seeds small or very small, very variously shaped; testa thin or spongy or corky, rarely mucilaginous; embryo undifferentiated
Annual or perennial herbs, terrestrial, epiphytic or aquatic, with much modified parts for the capture of small organisms
Herbaceous terrestrial, epiphytic or aquatic plants all with specialized organs for the capture of small organisms
Fruit a capsule, usually globose opening by valves or pores, circumscissile or indehiscent
Leaves rosulate or scattered on stolons, entire or divided, sometimes polymorphic
Ovary superior; style usually very short, persistent; stigma unequally 2-lipped
Leaves entire or much divided, often bearing traps
Ovules 2—numerous on a free central placenta
Seeds without endosperm, sometimes winged
Corolla 2-lipped, spurred or saccate
Flowers hermaphrodite, zygomorphic
Roots frequently absent
Calyx-lobes 2, 4 or 5
Flowers zygomorphic