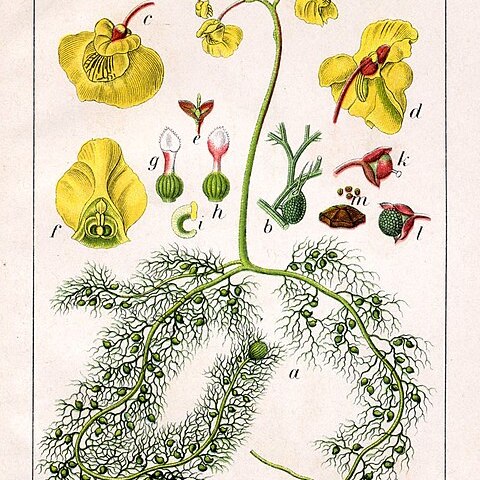
Annual or perennial aquatic terrestrial or epiphytic herbs always of damp places, without true roots or leaves but with stems modified in various ways to function as rhizoids, stolons and foliar organs, all species bearing small complex bladder-like traps for the capture and digestion of small aquatic organisms. Inflorescence racemose, peduncled, usually simple, bracteate; sterile bracts (scales) often present on the peduncle and sometimes also on the inflorescence axis; two bracteoles often present, almost always at the base of the pedicel, usually free, rarely ± connate with the bract. Bracts very varied, basifixed, medifixed or variously produced below the point of attachment. Calyx 2-lobed, usually ± accrescent, the lobes ± equal or variously dissimilar, usually free, sometimes ± connate at the base. Corolla bilabiate, yellow, various shades of violet or purple, white or rarely blue or red; upper lip entire or 2-or more-lobed; lower lip with an entire or 2-5-lobed limb, a ± raised, often gibbous palate and a usually subulate or conical spur, in a few species reduced to a short sac. Stamens 2 inserted at the base of the upper lip; filaments usually short, linear, often curved and often ± flattened and dilated above; anthers dorsifixed, ± ellipsoid, thecae ± confluent. Ovary globose or ovoid, ovules 2-many on a free basal or free central ± fleshy placenta; style usually short; stigma bilabiate, the lower lip usually much larger. Capsule globose or ovoid, dehiscing very variously by longitudinal slits, dorsiventral or rarely lateral valves, pores or circumscissile or rarely indehiscent. Seeds 1-many, very variously shaped and sculptured.
Herbs, annual or perennial, aquatic, terrestrial or epiphytic, always of damp places, without true roots or leaves but with stems modified in various ways to function as tubers, rhizoids, stolons, and + leaflike photosynthetic organs, all species bearing small complex bladderlike traps for the capture and digestion of small organisms. Inflorescences pedunculate, racemose, usually simple, brac-teate, sterile bracts (scales) often present on the peduncle and sometimes also on the inflorescence axis; bracts varied, basifixed, medifixed or variously produced below the point of insertion; bracteoles 2 or absent, rarely connate with the bract. Flowers with the calyx 2-lobed, usually accrescent; corolla usually spurred, yel-low or various shades of violet or purple, or white, rarely red, the upper lip en-tire or + 2-lobed, the lower lip entire or 2-5-lobed; stamens usually short, the filaments often winged, the anthers globose or ovoid; ovary ? globose, the ovules 2-many. Capsules globose to ovoid, dehiscing variously by longitudinal slits, dorsiventral or lateral valves or pores, circumscissile or indehiscent; seeds 1-many, variously shaped.
Herbs, perennial or annual, terrestrial, epiphytic, or aquatic, without true roots. Stems modified into rhizoids and stolons, rarely developed. Traps on rhizoids, stolons, and/or leaves, small, bladderlike. Leaves alternate or in a basal rosette, simple to many × divided, veins 1-3, unbranched, dichotomously branched, or pinnately branched. Inflorescences racemose or flowers solitary, pedunculate, usually simple, seldom branched, erect to twining, bracteate; bracts and bracteole often present, scalelike, sometimes basisolute (with base extending below point of insertion). Calyx parted from base into 2 equal or unequal lobes, lobes sometimes apically 2-parted. Corolla lower lip larger than upper lip; lower lip entire or 2-or 3(-6)-lobed, spurred, palate variously raised; upper lip entire or 2-or 3-lobed. Anther thecae confluent or distinct. Capsule adaxially loculicidal, both abaxially and adaxially loculicidal, or circumscissile, rarely indehiscent. Seeds few, many, or rarely 1 per capsule, variously appendaged.
Annual or perennial, aquatic, terrestrial or epiphytic herbs. Roots 0, but root-like structures present. Stems modified to form rhizoids, stolons and leafy shoots. Lvs usually small, entire when terrestrial or emergent, capillary and much-divided when submerged, all with small bladder-like traps. Infl. racemose, emergent in aquatic spp., usually with a simple scape or peduncle. Fls 1-several. Calyx 2-lipped, divided almost to base, usually accrescent. Corolla yellow, white or purple; upper lip entire or lobed, mainly small; lower lip entire or 2-5-lobed, generally larger than upper lip, with palate or pouch present at base, ± raised and often gibbous; spur usually subulate or conic. Filaments usually curved, often dilated and flattened; anthers convergent. Stigma unequally lobed. Ovules 1-numerous. Capsule globose or ovoid, dehiscing in various ways. Seed very variable in shape and sculpturing.
Inflorescence racemose, (but sometimes with a single flower) bracteate; peduncle usually simple, sometimes branched, usually filiform, erect or twining, usually glabrous, sometimes papillose, glandular or hairy, often provided (especially in the terrestrial species) with sterile bracts (scales); raceme usually elongated, rarely short and subcapitate; pedicels usually short, terete, flattened or more or less winged, often deflexed or decurved in fruit; bracts persistent, basifixed or produced below the point of insertion or peltate; bracteoles 2 or absent or sometimes more or less fused with the bract, inserted with the bract at the base of the pedicel or rarely with the calyx lobes at the apex of the pedicel.
Herbs, terrestrial or aquatic, affixed or freely suspended in water; stolons usually present (absent only in a few species, all Australian). Traps bladder-like, variously inserted on the vegetative parts, usually stalked, globose or ovoid; mouth basal, lateral or terminal, usually provided with appendages of very various kinds and closed by a door which bears on its outer surface varied glands or hairs. Inflorescence racemose or by reduction 1-flowered; peduncle often bearing sterile bracts (scales) between its base and the lowermost flower. Calyx lobes 2 or rarely 4.
Cal parted to the base into upper and lower segments, the upper often wider; cor bilabiate, the upper lip usually subentire or shallowly 2-lobed, the lower entire or 3-lobed, usually elevated at the base into a prominent palate, the tube prolonged at base into a spur or sac; herbs of water or wet soil, the lvs (lf-like branches?) linear and entire or variously dissected, in most spp. provided with small bladders that catch tiny aquatic animals; fls yellow or violet, in short racemes (or apparently solitary and terminal), each subtended by a small bract. 150, cosmop.
Scapes with 1-several fls; calyx deeply 2-lobed, segs often enlarging as capsule matures. Corolla spurred at back, 2-lipped; upper lip erect, entire or 2-lobed; lower lip spreading, us. 3-6-lobed; palate us. well-developed; stamens 2, ± curved; style short; stigma 2-lobed. Capsule subglobose, 2-valved, or dehiscing irregularly; seeds ∞. Herbs with filiform lvs and ∞ to few bladders that trap small animals. Widespread genus with some 250 spp. U. monanthos occurs also in Tasmania, and U. lateriflora in Tasmania and Australia. The other N.Z. spp. appear to be endemic.
Corolla bilabiate, glabrous, glandular or pubescent; throat closed or sometimes open; superior lip usually more or less erect, limb entire, emarginate or bilobed; inferior lip usually larger, spurred or rarely saccate at the base, palate usually raised and gibbous, limb spreading or deflexed, entire, emarginate or more or less deeply 2–5-lobed; spur more or less parallel to the inferior lip or divergent at an acute or obtuse angle or rarely in the same plane.
Calyx lobes 2, or rarely 4 in 2 decussate pairs, more or less equal or sometimes very unequal, usually free, sometimes more or less united at the base, persistent and usually accrescent, sometimes very markedly so; upper lobe usually entire, inferior lobe usually emarginate or bidentate, rarely both lobes dentate or fimbriate.
Foliar organs (leaves) either rosulate at the inflorescence base or alternate, opposite or verticillate on the stolons; in the terrestrial and epiphytic species mostly entire, erect or thalloid, capillary, linear, circular or peltate; in the aquatic species usually more or less dichotomously divided into capillary segments.
Traps rosulate, or lateral on the rhizoids, stolons or leaves or rarely terminal on the leaves, hollow, globose or ovoid, usually stalked, with a mouth which may be basal (adjacent to the stalk), lateral or terminal (opposite to the stalk); mouth usually provided externally with very diverse appendages.
Ovary globose or ovoid, unilocular; style usually short, often indistinct, persistent; stigma bilabiate, inferior lip usually much larger than the upper which may be obscure or obsolete; ovules 2-many, sessile on a more or less fleshy free basal placenta, anatropous.
Stem-like organs (stolons) arising with the rhizoids at the inflorescence base; in the terrestrial and epiphytic species usually short and delicate but sometimes developing into fleshy tubers; in the aquatic species usually more robust and longer.
Seeds 1-many, usually small or very small, globose, ovoid, truncate conical, narrowly cylindrical, fusiform, lenticular or prismatic, smooth, verrucose, reticulate, glochidiate, papillose or comose or variously winged.
Stamens 2, inserted at the base of the corolla; filaments straight or curved, usually twisted, sometimes winged; anthers dorsifixed, more or less ellipsoid, the thecae usually more or less confluent.
Vegetative parts not clearly differentiated but consisting of stems modified to function as roots, stems, leaves and specialized organs (traps) for the capture of small organisms.
Fruit a capsule, more or less globose or ovoid, dehiscing by longitudinal slits or by pores or circumscissile or indehiscent.
Root-like organs (rhizoids) usually descending from the base of the inflorescence, usually filiform.
Herbs, annual or perennial, terrestrial, epiphytic or aquatic.