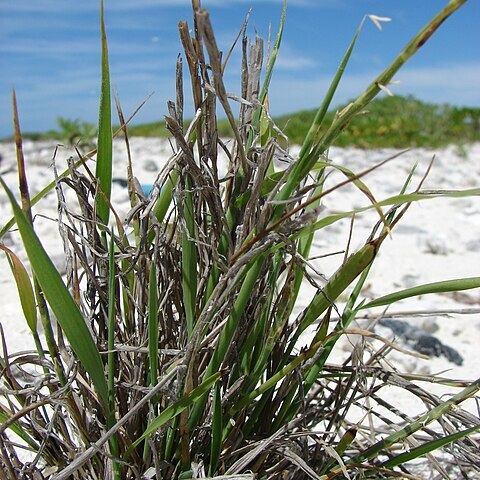
Perennial, stoloniferous, often very widely spreading. Culms tough, 20–50 cm tall, much branched. Leaf sheaths usually keeled, glabrous; leaf blades stiff, flat or involute, glaucous, 3–20 cm, 2.5–5 mm wide, glabrous or adaxially pilose near ligule, margins scabrous, apex acuminate; ligule 0.3–0.8 mm. Raceme erect, 5–15 cm; spikelets sometimes paired on each internode toward raceme base; rachis scabrous-hispidulous, internodes 3–5 mm. Spikelets 10–12 mm, florets often 2; lower glume membranous, triangular, up to 0.8 mm or absent; upper glume narrowly lanceolate, as long as spikelet, leathery, scabrous, apex caudate-aristate; lower lemma broadly lanceolate, 3.7–4.5 mm, puberulous near base, cartilaginous in lower two-thirds, thinner and scabrous above, apex acute. Anthers 1.5–2 mm. Caryopsis strongly dorsally compressed, plano-convex, 1.6–2 mm. 2n = 54.
Perennials. Flowering culms 10–60 cm high. Leaves: basal sheaths glabrous; collar glabrous; blade flat or convolute, 3–30 cm long, 2–10 mm wide, abaxially glabrous. Inflorescences 4–13 cm long; rachis glabrous. Spikelets opposite or alternate, 6–10 mm long, with 1 (–2) bisexual florets; rachilla prolongation 0.8–1.1 mm long. Upper glume narrowly oblong, 6–10 mm long, long-acuminate, muticous to awned (awn to 2 mm long), cartilaginous, 5–12-nerved, scaberulous or scabrous, glabrous. Basal lemma oblong to elliptic, 3.7–5 mm long, acute, entire, puberulous; hairs mainly arising in the upper half (longer at apex), very sparse on the lower half, appressed or spreading. Palea keels hairy for most of the length.
Spikelets 1-flowered, (8)10–14(22) mm long (the terminal up to 28 mm long); superior glume narrowly lanceolate to lanceolate or subulate, closely 8–12-nerved, smooth or minutely scaberulous, finely acute or acuminate, usually tipped with a rigid awn; lemma 4–5.5 mm long, ovate or ovate-oblong, minutely hairy at the base and sometimes also near the margins, obtuse; anthers 1.5–2.5 mm long.
Perennial 100-600 mm high; stoloniferous. Leaf blade to 150 x 2-10 mm. Inflorescence a fragile spike, spikelets sunk on opposite sides of the corky axis. Spikelet (8)10-14(22) mm long, dorsiventrally compressed; lower glume absent; upper glume longer than spike-let, awned; florets 1 to 2; lemma 4.0-5.5 mm long, obtuse; anther 1.3-1.5 mm long.
Stoloniferous perennial; culms up to 60 cm tall, slender, erect or ascending; leaf laminas up to 15 cm × 10 mm, linear to linear-lanceolate, flat or involute, stiff, glabrous or pilose towards the base, mostly glaucous, finely acute or pungent.
Raceme 4–20 cm long, straight or slightly curved, with internodes 3–7.5 mm long and 1.5–3 mm wide.