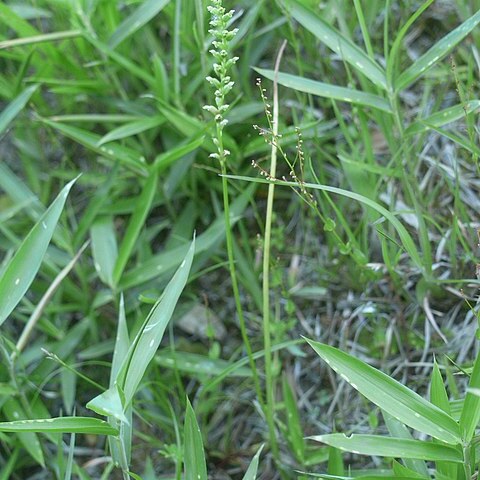
(Description based on specimens from Christchurch, New Zealand) Leaf 100–400 × 5–10 mm. Inflorescence 100–400 mm long, stiff, 10–100-flowered. Flowers crowded, 3–4 × 2.5–3 mm, green. Dorsal sepal porrect to obliquely erect, ovate to elliptic, c. 2.5 × 2 mm, concave, with short blunt apical mucro. Lateral sepals inrolled, oblong-tapered, c. 3 × 1 mm, shallowly curved, apex blunt. Petals erect within dorsal sepal, narrowly linear, c. 2 × 0.8 mm, shallowly curved, apex blunt. Labellum porrect at base then recurved, oblong to rectangular, c. 3 × 1.5 mm, margins constricted below middle, irregularly folded/crinkled, no cell-clusters, apex entire or shallowly notched. Basal callus of 2 dark green mounds; apical callus smaller, granular.
Plants 15-30 cm tall. Tuber small, 4-7 × 3-6 mm. Leaf erect or suberect, 16-33 × 0.2-0.3 cm, adaxially channeled. Inflorescence usually more than 10-flowered, emergent through opening in lower half of leaf; rachis 2.5-5 cm; floral bracts narrowly ovate-lanceolate, 1-2 mm. Flowers green or pale green; ovary and pedicel 2-3.5 mm. Dorsal sepal concave and forming a hood, broadly elliptic, ca. 2 × 1.5 mm, apex obtuse; lateral sepals suboblong or narrowly elliptic, ca. 1.5 × 0.8 mm. Petals narrowly oblong, ca. 1.2 × 0.5 mm, apex obtuse; lip narrowly elliptic-ligulate, 1.5-2 × ca. 1.2 mm, slightly fleshy, with notched callus at base. Column extremely short. Capsule elliptic, ca. 4 × 2-2.5 mm. Fl. and fr. May-Sep. 2n = 44, 88.
A robust orchid. The stem is 60 cm high. The leaf is 30-80 cm long and 0.9-1.2 cm wide. The leaf is long and like a tube. The leaf is dark green with a green base. The flower stem emerges through the side. It is 90 cm long. The flowers are pale green. There can be 100 flowers on one single flower spike. The spike is 2-15 cm long. The flowers are 0.4 cm across.