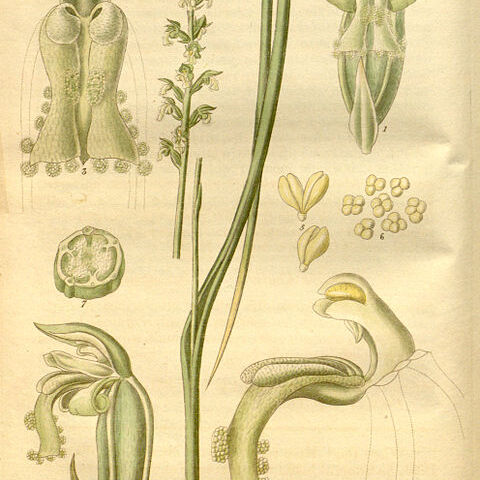
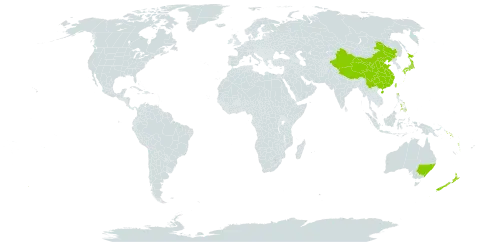
Raceme of few to many fls; floral bracts small, acute, hardly exceeding short pedicels. Per. glab., us. green; dorsal sepal uppermost in mature fls, broad and concave, much < ovary at fl.; lateral sepals almost equal in length but very much narrower, spreading or recurved, not connate; petals us. shorter and more obtuse, ± erect. Labellum about as long as other per.-segs, sessile, oblong to ovate, us. ± pendulous; calli us. paired at base, median and single near tip. Column short; wings membr., obtuse, attached to about mid-anther level; anther terminal, erect, almost entirely above stigma, ± hemispherical, pollinia not or obscurely bilobed, pollen granular; stigma broadly oval, slightly prominent; rostellum dark, its oval tip becoming detached with very short, threadlike stipe to which loosely coherent pollen masses adhere. Plants terrestrial, glab.; tuber globose to oval, often produced some distance from parent plant. Lf solitary; sheath long; lamina terete, ± hollow. Genus of perhaps a dozen spp., mainly Australian but extending also to S.E. Asia and to New Caledonia. N.Z. spp. probably all occur also in Australia.
Herbs, terrestrial, small. Tubers subglobose, to 1 cm in diam., fleshy; roots wiry, filamentous. Stem erect, slender, with membranous cataphylls at nodes. Leaf basal, solitary, cylindric, slender, hollow, glabrous, basally amplexicaul, sessile. Inflorescence terminal, racemose, with several to many flowers, emerging through opening in leaf; floral bracts small, sheathing. Flowers resupinate, small; ovary ribbed, glabrous; pedicel extremely short. Dorsal sepal free, erect, similar to but larger than lateral sepals, cucullate over column; lateral sepals free, spreading. Petals free, smaller than sepals; lip adnate to base of column, usually with basal callus adaxially, entire or sometimes apically emarginate, spurless. Column very short, fleshy, with 2 wings apically or laterally; anther erect, 2-locular; stigma entire, quadrate; pollinia 4, in 2 pairs, granular-farinaceous, with short caudicle and viscidium. Capsule erect.