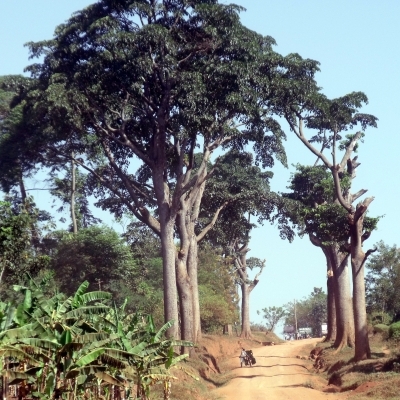
A large tree. It grows to 50 m tall. The bark is pale whitish grey. It is rough and scaly. It has buttresses. The trunk is straight. The leaves are simple and alternate. They are large and oblong. They are 12-18 cm long by 6.5-9.5 cm wide. They are green on top and paler and finely hairy underneath. The old leaves become bright yellow. The base of the leaf is lobed. The edges are wavy. The male and female flowers occur separately on separate trees. The male spike is long and slender. It is 6-14 cm long by 0.5 cm wide. The flowers are white. The female spikes are short and thick. They are 2-3 cm long by 1 cm wide. They are greenish. The fruit is a small nutlet. It has fleshy lobes around it. These occur close together like a mulberry.
Leaf lamina elliptic to oblong, 6–20(33) x 3.5–10(12) cm., subcoriaceous, chartaceous when juvenile, apex acuminate, base cordate to obtuse, margin subentire to repand, when juvenile serrate to crenate-dentate; superior surface glabrous or puberulous to pubescent on the main veins, when juvenile often scabridulous; inferior surface densely puberulous on the reticulum, pubescent to puberulous or almost glabrous on the main veins, when juvenile the whole surface hirtellous to tomentose; lateral veins 10–22 pairs, tertiary venation partly perpendicular to the lateral veins: petiole 1–5 cm. long; stipules 0.5–5 cm. long, caducous.
Pistillate inflorescences: spike 2–3 cm. long, c. 0.5 cm. in diam. (to 5 x 1.5 cm. in fruit); stigmas up to 7 mm. long.
Staminate inflorescences: spike 8–20 cm. long, c. 0.5 cm. in diam., peduncle 0.5–2.5 cm. long.
Fruit ellipsoid, 2.5–3 mm. long.
Tree up to 30(50) m. tall.