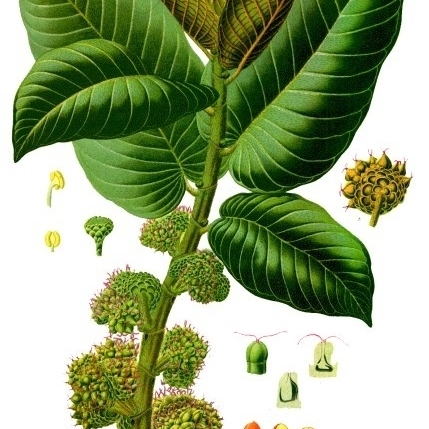
Trees, shrubs, herbs, or vines , deciduous or evergreen, frequently with milky sap. Leaves alternate (rarely opposite or whorled), simple; stipules present, persistent or caducous; petiole adaxially grooved. Leaf blade: margins entire, toothed, or lobed; venation pinnate or with 3-5 basal palmate veins; cystoliths often present in epidermal cells. Inflorescences racemes, cymes, or capitula. Flowers unisexual, staminate and pistillate on same or different plants, small, occasionally on flattened torus, more often enclosed within fleshy, flask-shaped receptacle (syconium); sepals 2-6, distinct or partly connate (vestigial in Brosimum ). Staminate flowers: stamens equal in number to sepals or calyx lobes and opposite them, straight or inflexed; anthers 1-2-locular. Pistillate flowers: sepals or calyx lobes 4, ± connate; pistils 1, 1-2-carpellate; ovary 1, superior or inferior, 1(-2)-locular; ovules 1 per locule; styles or style branches 1-2; stigmas 1-2, entire. Fruits multiple (syncarps); individual achenes or drupelets partly or completely enclosed by enlarged common receptacle or by individual calyces.
Shrubs, trees, climbers or herbaceous plants, monoecious or dioecious, usually with milky latex. Leaves alternate or opposite, simple, or (not in Australia) pinnate or palmate, usually with cystoliths, stipulate. Inflorescence axillary, unisexual or bisexual, paniculate, racemose, spicate, discoid, capitate or urceolate. Flowers small, unisexual, apetalous. Tepals usually 4, or up to 8, free or united, imbricate or valvate, persistent, or absent. Stamens opposite tepals, or reduced to 3, 2 or 1; filaments straight, free or connate, or inflexed; anthers large and mucronate, to small, bilobate and non-mucronate. Ovary superior, inferior or immersed in sockets in inflorescence, usually 1-locular; styles 1 or 2; stigma simple or bifid; ovule 1, anatropous or campylotropous, generally apical. Pistillode present or absent in male flowers. Fruit drupaceous, free, or connate in fleshy syncarps or syconia (figs), or achenes. Seeds small to large, with endocarp; testa membranous or disintegrated; embryo curved or straight; cotyledons plicate, conduplicate, or flat.
Trees, shrubs or herbs, dioecious or monoecious; sap milky, sometimes watery (but not turning black). Leaves in spirals or distichous, sometimes subopposite or subverticillate, entire or sometimes pinnately or palmately incised, stipulate. Inflorescences bisexual or unisexual, spicate, globose-, clavate-or discoid-capitate, urceolate or uniflorous. Staminate flowers with 2–6 tepals or perianth lacking; stamens 1–4. Pistillate flowers with 2–6 tepals or perianth lacking; pistil 1; ovary free or adnate to the perianth; stigmas 1–2; ovule 1, attached apically. Fruit achene-like, drupaceous (dehiscent or not), or forming a drupaceous whole with the fleshy perianth or with the fleshy receptacle as well. Seed large without endosperm or small with endosperm; embryo various
Female flower with superior or inferior ovary, of 2 carpels, one often abortive, usually 1-celled; styles mostly 2, filiform; ovule solitary, pendulous, rarely basal and erect
Pistillate flowers with 2–6 tepals or perianth lacking; pistil 1; ovary free or adnate to the perianth; stigmas 1 or 2, ovule 1, apically attached
Leaves spirally or distichously arranged, sometimes subopposite or subverticillate, entire or sometimes pinnately or palmately incised, stipulate
Fruit achene-like, drupaceous (dehiscent or not), or forming a drupaceous whole with the fleshy perianth or with the fleshy receptacle as well
Inflorescence bisexual or unisexual, spicate, globose, clavate-or discoid-capitate, urceolate, sometimes uniflorous
Stamens usually equal in number and opposite to the sepals; filaments inflexed or erect in bud; anthers 2-celled
Trees, shrubs or herbs, dioecious or monoecious; sap milky, sometimes watery (but not turning black)
Leaves alternate, rarely opposite, simple; stipules paired, often caducous and leaving a scar
Flowers much reduced, often in heads, disks or hollow receptacles, unisexual
Seed large and without endosperm or small with endosperm, embryo various
Staminate flowers with 2–6 tepals or perianth lacking; stamens 1–4
Calyx-lobes usually 4, sometimes reduced, imbricate or valvate
Seed with or without endosperm, often with curved embryo
Trees or shrubs or rarely herbs, often with milky juice
Fruit a small achene, nut or drupe