Trees, shrubs, climbers, stranglers, or sometimes woody epiphytes, evergreen or deciduous, with latex; monoecious species with male, gall (sterile female), and female flowers in each fig or dioecious with either male and gall flowers or only female flowers in each fig. Stipules often connate, lateral to amplexicaul and enclosing terminal leaf bud, caducous or ± persistent, scar ringlike. Leaves usually alternate, rarely opposite or ± verticillate; leaf blade simple to lobed, rarely palmate, glabrous or hairy, abaxially usually with waxy spots (“wax glands”) at base of leaf blade or in axil of secondary veins, with or without papillalike cystoliths, margin entire or toothed; veins pinnate to ± palmate. Inflorescences axillary or on specialized cauliflorous branches, a fig (syconium) with many minute flowers inserted on inner wall of hollow receptacle communicating with outside through an apical pore or apical pore closed by scale-like bracts, sessile or pedunculate; involucral bract usually 3 at base of fig; lateral bracts sometimes present on side of fig, scale-like, caducous or persistent. Male flowers: calyx lobes 2-6; stamens 1-3 (rarely more), straight in bud; pistillode present or absent. Gall flowers: similar to female flowers but never producing seeds and usually occupied by a fig wasp. Female flowers: calyx lobes 0-6; ovary free, straight or oblique; styles 1 or 2 and unequal, apical or lateral. Fruit a seedlike achene, usually enclosed within syncarp formed from an enlarged hollow fleshy receptacle. Seeds pendulous; endosperm usually scanty; cotyledons equal or unequal, sometimes folded.
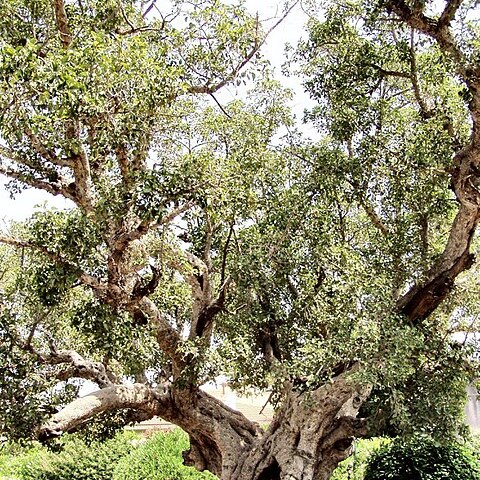
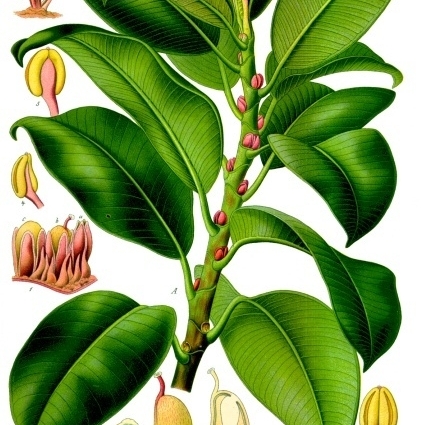
A genus (at least so far as the American species are concerned) of soft-wooded, generally smooth-barked trees and shrubs with milky or opalescent latex. Many species begin life as epiphytes, or epiliths, which may eventually, through the coalescence of their roots, completely encircle the trunk of, and strangle, their host. Leaves entire and spiral in native species-rarely opposite and sometimes toothed or lobed in the Old World. Stipules long or short, enfolding the buds, generally quickly deciduous but rarely persistent, leaving a scar surrounding the stem. Flowers unisexual, borne over the inner surface of a hollow, globose, more or less fleshy structure (the receptacle or "fig") the apical pore (ostiole or orifice) of which is closed by a series of interlocking bracts. The female flowers are of two kinds: functional females, generally sessile and maturing into viable achenes, and sterile females (gall flowers), generally stalked and functioning as incubators for the larvae of a wasp which pollinates the fertile flowers. Male, female and gall flowers are completely intermixed in American species. The figs are generally solitary or paired, borne among the leaves but sometimes on specialized short shoots behind the leaves in American species. In Old World species they may be borne similarly or in leafless racemes or panicles on the trunk and larger branches.
Trees or shrubs, monoecious, terrestrial or hemi-epiphytic and then with aerial roots and often strangling (the host tree). Leaves alternate in spirals; stipules fully amplexicaul, free; blade entire, pinnately veined, with one or two (waxy) glandular spots at the base of the primary vein beneath. Inflorescences (figs, syconia) solitary, or in pairs in the leaf axils, or just below the leaves or on spurs in the leaf axils and on the older wood, bisexual, pedunculate or sessile, receptacle urceolate, subtended by 2 or 3 bracts (= basal bracts), the apical opening (ostiole) closed by interlocking bracts. Staminate flowers numerous to several, tepals 2-6, free or basally connate; stamens 1 or 2; pistillode absent or present. Pistillate flowers numerous, pedicellate or sessile; tepals 2-4, free or basally connate; ovary free, stigmas 1 or 2; pistillate flowers more or less differentiated into seed flowers (to produce seeds) and gall flowers (to hatch the larvae of fig wasps, the pollinators), seed flowers often (sub)sessile and with relatively long styles, gall flowers usually pedicellate, with relatively short styles. Fruiting perianth hardly enlarged, membranous; fruits free, achenes or slightly drupaceous; seeds small, with endosperm, cotyledons flat and equal.
Trees, shrubs, or woody vines , evergreen or deciduous, commonly epiphytic or scandent as seedlings; sap milky. Terminal buds surrounded by pair of stipules. Leaves alternate, monomorphic (dimorphic in F . pumila ); stipules caducous, fused, enclosing naked buds. Leaf blade: margins entire (lobed in F . carica ), rarely dentate; venation pinnate or nearly palmate. Inflorescences small, borne on inner walls of fruitlike and fleshy receptacle (syconium). Flowers: staminate and pistillate on same plant. Staminate flowers sessile or pedicellate; calyx of 2-6 sepals; stamens 1-2, straight. Pistillate flowers sessile; ovary 1-locular; style unbranched, lateral. Syconia globose to pyriform; achenes completely embedded in enlarged, fleshy, common receptacle and accessible by apical opening (ostiole) closed by small scales. x = 13.
Trees, monoecious or dioecious; internodes not distinctly different in length and leaves not tufted. Leaves spirally arranged and lamina symmetric, lamina (sub)coriaceous to chartaceous; cystoliths only beneath; waxy glands in the axils of the basal lateral veins or additional ones elsewhere on the lamina beneath (or on the nodes of leafy twigs); petiole (rather) long. Figs cauliflorous, flagelliflorous, or axillary; basal bracts 3, verticillate; lateral bracts absent. Staminate flowers subtended by 2 bracteoles; stamens (1 or) 2 (or 3). Tepals of pistillate flowers (2-)3-6, free or connate, often irregularly in shape, laciniate and/or narrow, glabrous; styles of long-styled flowers glabrous (or hairy). Fruits lenticular, slightly simply, keeled, smooth or ± tuberculate, red-brown (or whitish).
Trees or shrubs, sometimes epiphytic stranglers or root-climbers. Leaves simple, entire or palmately lobed, usually petiolate; glands often present on underside of leaves, in axils of veins or apex of petiole. Inflorescence (fig) urceolate, axillary, cauliflorous or on underground stolons. Tepals 2–8, free or connate, entirely gamophyllous or absent. Male flowers: stamens 1–8; anthers mucronate, introrse; pistillode usually absent. Female flowers: ovary 1, unilocular; style subterminal to gynobasic; stigma bifid or simple; ovule 1, anatropous. Gall flower with a bloated sterile ovary containing a fig-wasp; style short; stigma funnel-shaped. Fruit a drupelet, the woody endosperm forming a pyrene.
Monoecious, rarely dioecious, trees, shrubs or creepers, not armed, sometimes epiphytic. Lvs usually alternate, rarely opposite, entire or lobed; venation pinnate or palmate. Stipules caducous, leaving an amplexicaul scar. Infl. fleshy, globose to obovoid or turbinate, with an ostiole at the apex and enclosing usually very numerous, small ♂ and ♀ fls; sterile gall fls used as oviposition sites also often present. ♀ fls stalked or sessile. Calyx of ♂ fls 2-6-lobed or partite, rarely reduced to 1 scale; stamens 1-2-(6), erect in bud. Calyx of ♀ fls often with fewer, narrower divisions than in ♂, or minute or 0; ovules pendulous. Achenes enclosed in the enlarged receptacle; endosperm often scanty.