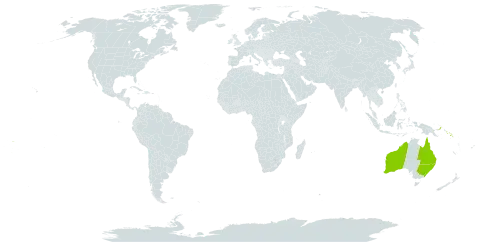
Tree up to 40 m tall, hemi-epiphytic (or terrestrial?). Leafy twigs 1-5 mm thick, angular, minutely puberulous or glabrous. Leaves spirally arranged; lamina elliptic to oblong, (2.5-)3.5-13 by (0.8-)1-5 cm, coriaceous, apex (sub)acuminate, the acumen blunt to sharp, base cuneate; upper glabrous, lower surface glabrous; cystoliths on both sides or only above; lateral veins 10-15 pairs, the basal lateral veins hardly distinct, tertiary venation parallel to the lateral veins; waxy gland at the base of the midrib; petiole 0.5-2.5 cm long, glabrous; stipules 1-2.5(-3) cm long, minutely puberulous or glabrous, caducous. Figs axillary, in pairs or solitary; subsessile or with a peduncle up to 0.5 cm long, dilated; basal bracts 3, 1-5 mm long, cucullate, glabrous or sparsely minutely puberulous, early caducous; receptacle subglobose, 0.3-1 cm diam. when dry, glabrous, orange at maturity, maculate, apex slightly umbonate, ostiole tri-radiate (to almost slit-shaped); inner layer of the wall thin. Fruits basally embedded in the swollen pedicels.
A strangling fig tree which can grow 15 to 30 m high. It can spread 15-30 m wide. When grown in the open it has a rounded spreading crown. The trunk has buttresses. The bark is grey-brown. The leaves are dark green and dense. They are paler underneath. The leaves are simple and 6-10 cm long by 2-3.5 cm wide. The mature leaves are smooth. The fruit are 6-10 mm across. They occur in clusters in the axils of leaves. The fruit are edible. Some varieties occur.