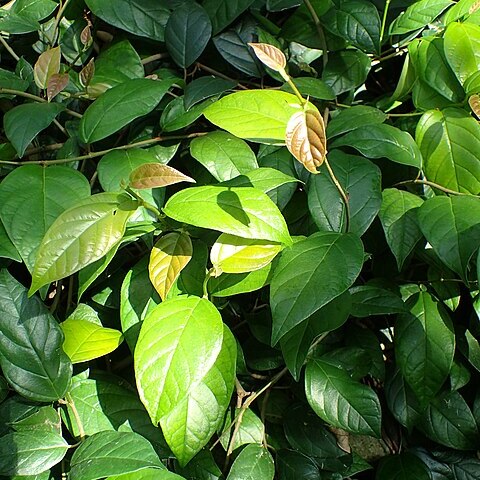
Root-climber. Branchlets drying brown. Leafy twigs 2-5 mm thick, hollow or solid, ribbed, strigillose to hirtellous to puberulous to glabrous. Leaves distichous; lamina elliptic to oblong to (sub)ovate, (4-)10-20(-30) by (1.5-)5-10(-14) cm, symmetric, coriaceous, apex acuminate to acute, base (almost) equilateral, cordate to rounded (or to cuneate), margin entire, flat to revolute; upper surface glabrous or sparsely strigillose or also puberulous on the midrib, glabrescent, lower surface sparsely (to rather densely) strigillose on the main veins or only the midrib or also puberulous, sometimes only appressed-puberulous; cystoliths on both sides; midrib prominent, the main veins sometimes slightly impressed and then the midrib raised as a narrow ridge in the impression above, lateral veins (5-)6-9(-10) pairs, slightly prominent beneath, the basal pair up to 1/6-1/3 the length of the lamina, branched (or unbranched), the other lateral veins sometimes furcate far from the margin, tertiary venation scalariform, slightly prominent beneath, the smaller veins (almost) flat beneath; waxy glands in the axils of the basal lateral veins and usually also in the axils of some other lateral veins and in the axils of branches and in furcations of the lateral veins (or absent); petiole (0.5-)1-4 cm long, sparsely strigillose or partly puberulous (or hirtellous), the epidermis flaking off; stipules (0.5-)1-1.5 cm long, yellowish subsericeous or sparsely to densely minutely puberulous and/or brown strigillose only on the keel and at the base (or glabrous), caducous or subpersistent. Figs axillary and on up to 0.5 cm long spurs on the older wood, in pairs, solitary, or clustered; with a peduncle up to 0.5 cm long or sessile; basal bracts 0.5-2 mm long, caducous (or subpersistent); receptacle subglobose, (0.3-)0.5-1(-1.2) cm diam. when dry, 1.5-2 cm diam. when fresh, 0.1-0.7 cm long stipitate, glabrous or sparsely minutely puberulous, surface often ± pustulate, yellow to red to crimson or to purple at maturity, apex convex to slightly umbonate, ostiole 0.5-1 mm diam., slightly sunken, flat or slightly prominent, often surrounded by a rim; internal hairs few and small. Tepals red.
More
Trees when mature, epiphytic vine when young. Branchlets pubescent, glabrescent, nodes with short roots. Stipules caducous, ovate-lanceolate, pubescent. Petiole ca. 1.5 cm, sparsely pubescent; leaf blade ovate to ovate-elliptic, 7-13(-20) × (3-)5-10(-14) cm, leathery, base rounded, ± cordate, or cordate, margin entire or slightly undulate, apex acute to mucronate; veins abaxially with hairs when young, glabrescent; basal lateral veins 2 or 4, secondary veins 5 or 6 on each side of midvein. Figs axillary on leafy or on leafless branchlets, solitary or paired, occasionally in clusters or on shortly tuberculate branchlets from leafless branches, reddish orange when mature, ± globose, 0.8-1.5 cm in diam., hairy when young, base attenuate into a short stalk, inside without bristles, apical pore navel-like; peduncle short; involucral bracts caducous. Male flowers: near apical pore; calyx lobes 3; stamens 2; filaments connate; anthers mucronate. Gall flowers: calyx lobes 3; ovary obovoid; style lateral, short. Female flowers: calyx basally connate, apically 3-lobed; style lateral, long; stigma cylindric. Achenes ellipsoid. Fl. Dec-Mar.