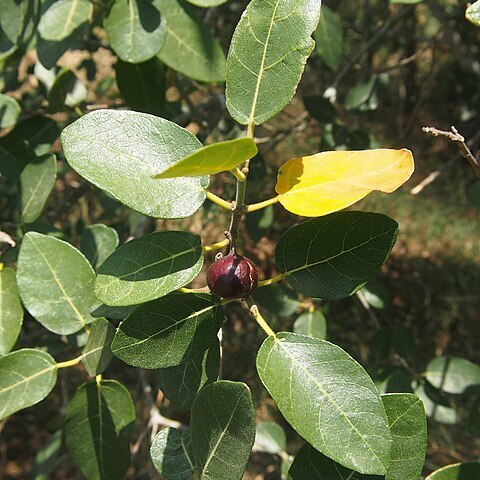
Shrub or tree up to 15 m tall. Branchlets often drying red-brown. Leafy twigs 1.5-4 mm thick, whitish puberulous to hispidulous or (sub)tomentose, smooth to scabridulous; internodes hollow or solid. Leaves (sub)opposite or alternate (sub)distichous or in laxly spirals (or subverticillate); lamina oblong to elliptic to subovate or to subobovate (or to lanceolate), 4-16 by 1.5-8 cm, (almost) symmetric, subcoriaceous to chartaceous, apex acuminate (mostly with a relatively short and blunt acumen, sometimes with a relatively long and acute acumen) to rounded (to emarginate), base (almost) equilateral, cuneate to rounded to subcordate, margin entire to ± irregularly crenate-denticulate, often ± revolute; upper surface (minutely) hispidulous, scabrous, lower surface minutely whitish hispidulous or (sub)tomentose on the veins, scabrous or smooth; cystoliths on both sides; lateral veins (4-)6-9 pairs, the basal pair up to 1/6-1/3 the length of the lamina, mostly running close to the margin of the lamina and then unbranched, often other lateral veins, in particular in the upper part of the lamina, furcate, tertiary venation scalariform; waxy glands in the axils of both basal lateral veins or extended to or on the midrib and then often fused; petiole 0.8-2(-4) cm long, slightly different to almost equal in length on the same twig, whitish hispidulous or (sub)tomentose, the epidermis persistent; stipules semi-amplexicaul, chartaceous, 0.3-0.5(-0.8) cm long, sparsely puberulous, caducous. Figs axillary and also just below the leaves, in pairs or solitary; peduncle 0.2-1 cm long; peduncular bracts 3, scattered (up to the base of the receptacle) or verticillate, 0.5-1 mm long; receptacle (sub)globose, 0.8-1.2 cm diam. when dry, 1.5-2 cm diam. when fresh, minutely hispidulous, scabrous, mostly without lateral bracts, purple-black at maturity, apex convex, ostiole 1.5-2 mm diam.; internal hairs abundant, brownish. Tepals whitish, glabrous, or hairy at the apices. Styles glabrous.
More
Tree to 8 m high. Leaves opposite, often decussate, sometimes alternate; lamina ovate, oblong to ± orbicular, 4–14 cm long, 3–6 cm wide, rounded to cordate at base, often sinuate with small rigid hairs, acute to obtuse at apex, variously hairy, often strongly scabrid; lateral veins 8–10 pairs, the basal pair often more distinct; petiole 5–30 mm long, usually pubescent to villous, rarely glabrescent; stipules to 1 cm long. Figs globular, 1–1.5 cm diam., glabrescent-scabrid to densely villous; ostiole slightly umbonate, with protruding apical bracts; lateral bracts often present; basal bracts variously arranged. Flowers with 5–7 tepals. Male flowers in a single row; stamens 1 or 2. [var. opposita: Leaf lamina 6–14 cm long, 4–6 cm wide; petiole 10–30 mm long. Figs 10–15 mm diam.] [The above description from the Flora of Australia Volume 3 Ficus treatment (Chew 1989) requires revision since it included Ficus opposita var. micracantha (Miq.) Corner which is now treated as Ficus aculeata A.Cunn. ex Miq. See Dixon (2007: 280–282) and Zich et al. (2020) for more recent description of F. opposita-Editor, 19 August 2021.]
A fig. It is an evergreen shrub or small tree. Trees can lose all their leaves in the dry season. It grows to 5-8 m high and spreads to 2-4 m across. The stem is erect and branching. It mostly has a rounded crown. The bark is rough, dark grey and deeply cracked along its length. It does not have aerial nor strangling roots. The leaves are produced opposite one another. They are stiff and coarse. They are oval or heart shaped and 3-11 cm long by 2.5-5.5 cm wide. Leaves can be larger and vary in shape. Young leaves can be of different shapes. They are hairy underneath. The edge of the leaf is wavy or finely toothed. The leaf stalk is hairy and 0.5-2 cm long. Trees are separately male and female. The fruit or figs are carried either singly or in pairs. They start pear shaped but become round. They are 1-2.5 cm across. They are green but turn red-brown to black when ripe. They are produced in the axils of leaves or just below the leaves. They are borne singly or in pairs.
"Essentially a woodland species found predominantly in open eucalypt communities and is also commonly encountered in riparian vegetation bordering eucalypt communities. It has also been recorded from deciduous vine thickets, fringes of rain forest and coastal sand dune communities. It has been collected from a variety of soil types including soils derived from basalt, sandstone, granite, limestone, alluvial deposits and serpentine."
More
It grows in tropical, subtropical and warm temperate locations. It does best in a rich well drained soil. It needs a protected partly shaded position. It is drought and frost tender. It grows from sea level to 750 m above sea level.