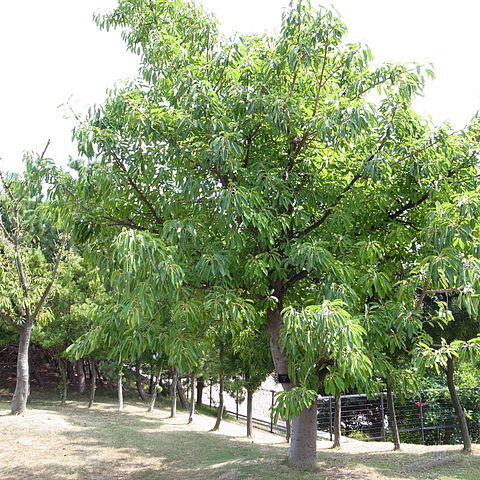
Tree up to 30 m tall, hemi-epiphytic, deciduous. Branches drying pale brown to blackish. Leafy twigs (3-)5-12 mm thick, subterete, minutely white puberulous to subglabrous. Leaves spirally arranged; lamina oblong to elliptic to (sub)ovate (to lanceolate), 8-25 by 3-13.5 cm, (sub)coriaceous, apex (short-)acuminate, the acumen mostly blunt, base rounded to subcordate (or to obtuse to cuneate); both surfaces glabrous; cystoliths only beneath; lateral veins 7-10 pairs, often furcate far from the margin, the basal pair up to 1/10-1/4 the length of the lamina, unbranched, tertiary venation reticulate to partly parallel to the lateral veins; waxy gland at the base of the midrib, in dry material often in a groove at the base of the midrib; petiole 4-10(-20) cm long, glabrous, the epidermis persistent; stipules (0.5-)0.8-1.5 (on opening shoots up to 7) cm long, densely white woolly-tomentose to-subvillous, caducous or subpersistent at the apices of the twigs and forming ovoid terminal buds. Figs ramiflorous on up to 1 cm long curved spurs, 1-5 together; peduncle 0.7-1.5 cm long, densely minutely puberulous; basal bracts 3, 3-5 mm long, puberulous, caducous; receptacle subglobose to subpyriform, 0.8-1.2(-1.5) cm diam. when dry and the surface wrinkled, sparsely minutely puberulous to glabrous, at maturity turning from white to pink to purple to black, apex convex to flat, ostiole 2-3 mm diam., ± prominent, the upper ostiolar bracts glabrous; internal hairs absent. Staminate flowers near the ostiole. Tepals reddish. Ovary red-brown.
More
A large fig. It loses its leaves for a short time. It has some aerial roots. It grows 6-21 m high and spreads 10-18 m wide. The young leaves are pink. They become mid green. The leaves grow to 25 cm long. The figs are dull purple. They are 18 mm across. They are clustered on short stalks.