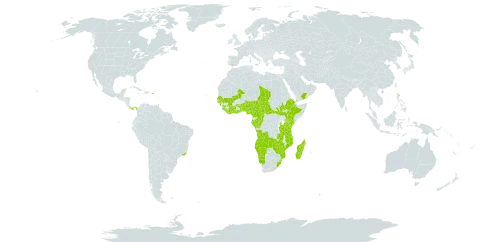
Tree up to 20(25) m tall, hemi-epiphytic or secondarily terrestrial, with a spreading crown. Leafy twigs 5-12(20) mm thick, puberulous, white to yellow tomentose, hirsute or subvillous, or glabrous, periderm flaking off when dry. Leaves spirally arranged; lamina elliptic to oblong or subobovate, 7-25(45) x 3-12(20) cm, coriaceous; apex acuminate; base obtuse, cuneate or subcordate; margin entire; superior surface glabrous, puberulous on the midrib, inferior surface puberulous to hirtellous or glabrous, the main veins ± tomentose-hirsute below; lateral veins (4)6-10(12) pairs, tertiary venation partly scalariform to reticulate; petiole 1.5-13(17) cm long, 2-4(8) mm thick, epidermis flaking off when dry; stipules 5-25 mm long, up to 80 mm long on new flush, puberulous or white-to yellow-subsericeous, caducous. Figs up to 4 together in the leaf axils or just below the leaves, sessile, initially enclosed in a white-pubescent to subhirsute calyptrate bud up to 0.5 cm long; basal bracts 3-6(8) mm long, persistent. Receptacle subglobose, c. 10-25(35) mm in diam. when fresh, 8-15(25) mm in diam. when dry, puberulous to white-or yellow-pubescent to subhirsute, smooth or verruculose, yellow to orange or brownish at maturity.
A strangler fig. It often grows attached to other plants. It can grow to a large tree. It grows 18 m high. It can spread 12 m wide. The trunk can be 3 m around. The crown is very wide and round. It can have aerial roots. The bark is grey brown. The leaves are large and evergreen. The leaves are dark green and slender. They are 38 cm long by 20.5 cm wide. They are crowded near the ends of branches. The leaf stalks are 2-8 cm long. The tip is pointed and the base is rounded. The leaf stalk is 12 cm long. The leaves are in spirals on stout small branches. The figs are small and orange-red when ripe. They are crowded closely together along the ends of the branches. They are 1-1.7 cm across.
Leaves spirally arranged; lamina elliptic to oblong or subobovate, 7–25(45) x 3–12(20) cm., coriaceous; apex acuminate; base obtuse, cuneate or subcordate; margin entire; superior surface glabrous, puberulous on the midrib, inferior surface puberulous to hirtellous or glabrous, the main veins ± tomentose-hirsute below; lateral veins (4)6–10(12) pairs, tertiary venation partly scalariform to reticulate; petiole 1.5–13(17) cm. long, 2–4(8) mm. thick, epidermis flaking off when dry; stipules 5–25 mm. long, up to 80 mm. long on new flush, puberulous or white-to yellow-subsericeous, caducous.
Receptacle subglobose, c. 10–25(35) mm. in diam. when fresh, 8–15(25) mm. in diam. when dry, puberulous to white-or yellow-pubescent to subhirsute, smooth or verruculose, yellow to orange or brownish at maturity.
Figs up to 4 together in the leaf axils or just below the leaves, sessile, initially enclosed in a white-pubescent to subhirsute calyptrate bud up to 0.5 cm. long; basal bracts 3–6(8) mm. long, persistent.
Leafy twigs 5–12(20) mm. thick, puberulous, white to yellow tomentose, hirsute or subvillous, or glabrous, periderm flaking off when dry.
Tree up to 20(25) m. tall, hemi-epiphytic or secondarily terrestrial, with a spreading crown.